Introduction
The scop package provides a comprehensive set of tools for single-cell omics data processing and downstream analysis:
- Integrated single-cell quality control methods, including doublet detection methods (scDblFinder, scds, Scrublet, DoubletDetection).
- Pipelines embedded with multiple methods for normalization, feature reduction (PCA, ICA, NMF, MDS, GLMPCA, UMAP, TriMap, LargeVis, PaCMAP, PHATE, DM, FR), and cell population identification.
- Pipelines embedded with multiple integration methods for scRNA-seq, including Uncorrected, Seurat, scVI, MNN, fastMNN, Harmony, Scanorama, BBKNN, CSS, LIGER, Conos, ComBat.
- Multiple methods for automatic annotation of single-cell data (CellTypist, SingleR, Scmap, KNNPredict) and methods for projection between single-cell datasets (CSSMap, PCAMap, SeuratMap, SymphonyMap).
- Multiple single-cell downstream analyses:
- Differential expression analysis: identification of differential features, expressed marker identification.
- Enrichment analysis: over-representation analysis, GSEA analysis, dynamic enrichment analysis.
- Cellular potency: CytoTRACE 2 for predicting cellular differentiation potential.
- RNA velocity: RNA velocity, PAGA, Palantir, CellRank, WOT.
- Trajectory inference: Slingshot, Monocle2, Monocle3, identification of dynamic features.
- Cell-Cell Communication: CellChat for cell-cell communication.
- High-quality data visualization methods.
- Fast deployment of single-cell data into SCExplorer, a shiny app that provides an interactive visualization interface.
The functions in scop are all developed around the Seurat object and are compatible with other Seurat functions.
Quick Start
-
scop: Single-Cell Omics analysis Pipeline
- Introduction
- Quick Start
- Credits
-
Installation
- R version requirement
- Prepare python environment
- Data exploration
- CellQC
- Standard pipeline
- Integration pipeline
- Cell projection between single-cell datasets
- Cell annotation using bulk RNA-seq datasets
- Cell annotation using single-cell datasets
- Cellular potency
- Velocity analysis
- Trajectory inference
- Dynamic features
- Differential expression analysis
- Enrichment analysis(over-representation)
- Enrichment analysis(GSEA)
- Interactive data visualization with SCExplorer
- Other visualization examples
Credits
The scop package is developed based on the SCP package, making it compatible with Seurat V5 and adding support for single-cell omics data.
Installation
R version requirement
- R >= 4.1.0
You can install the latest version of scop with pak from GitHub with:
if (!require("pak", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("pak")
}
pak::pak("mengxu98/scop")Prepare python environment
To run functions such as RunPAGA(), RunSCVELO(), scop requires conda to create a separate python environment. The default environment name is "scop_env". You can specify the environment name for scop by setting options(scop_envname = "new_name").
Now, you can run PrepareEnv() to create the python environment for scop. If the conda binary is not found, it will automatically download and install miniconda.
scop::PrepareEnv()To force scop to use a specific conda binary, it is recommended to set reticulate.conda_binary R option:
options(reticulate.conda_binary = "/path/to/conda")
scop::PrepareEnv()If the download of miniconda or pip packages is slow, you can specify the miniconda repo and PyPI mirror according to your network region.
scop::PrepareEnv(
miniconda_repo = "https://mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn/anaconda/miniconda",
pip_options = "-i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple"
)Available miniconda repositories:
https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda (default)
Available PyPI mirrors:
https://pypi.python.org/simple (default)
Data exploration
The analysis is based on a subsetted version of mouse pancreas data.
library(scop)
data(pancreas_sub)
print(pancreas_sub)
#> An object of class Seurat
#> 47886 features across 1000 samples within 3 assays
#> Active assay: RNA (15962 features, 2000 variable features)
#> 3 layers present: counts, data, scale.data
#> 2 other assays present: spliced, unspliced
#> 2 dimensional reductions calculated: pca, umap
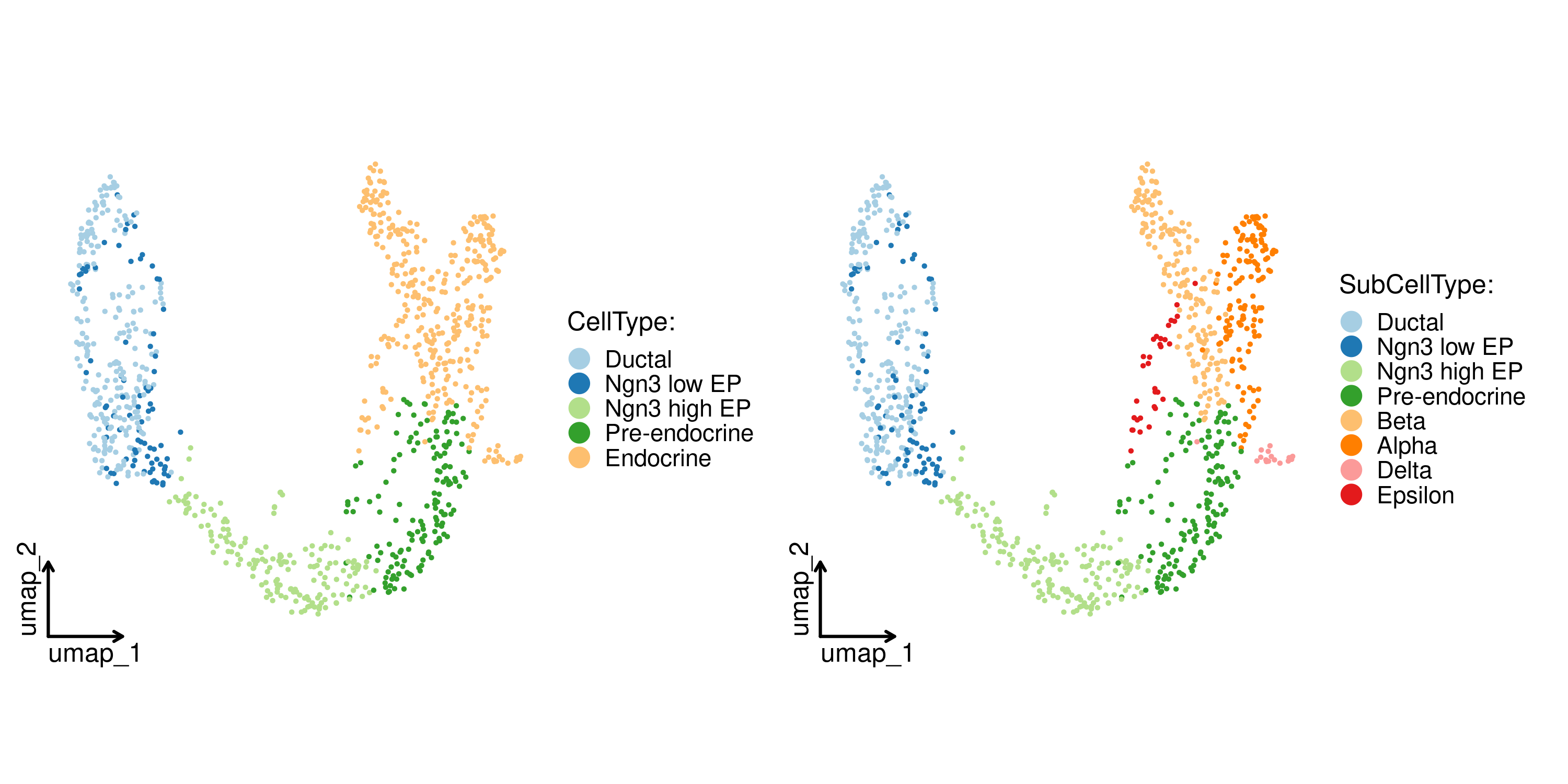
CellDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = c("CellType", "SubCellType"),
reduction = "UMAP",
theme_use = "theme_blank"
)
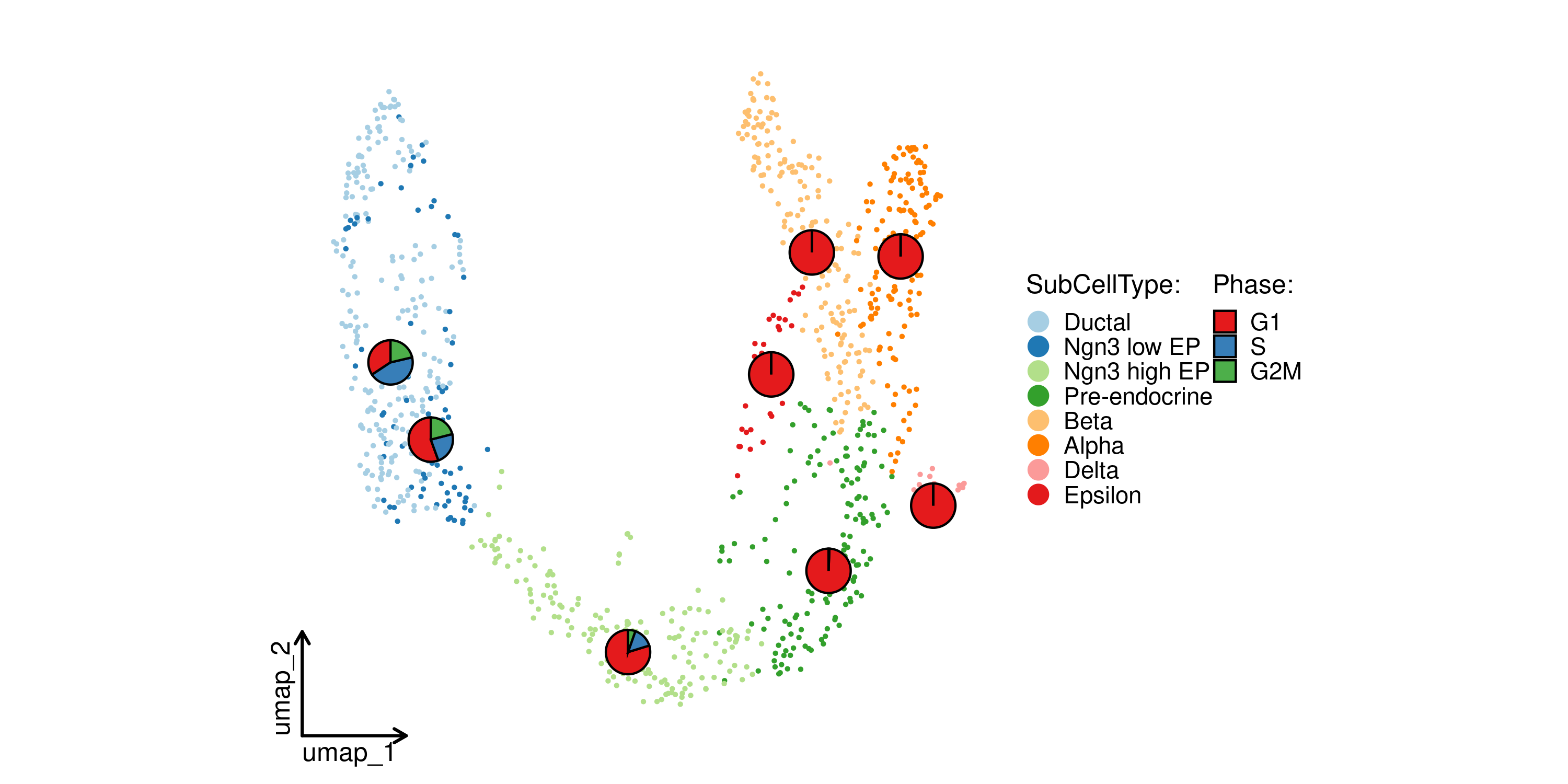
CellDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "SubCellType",
stat.by = "Phase",
reduction = "UMAP",
theme_use = "theme_blank"
)
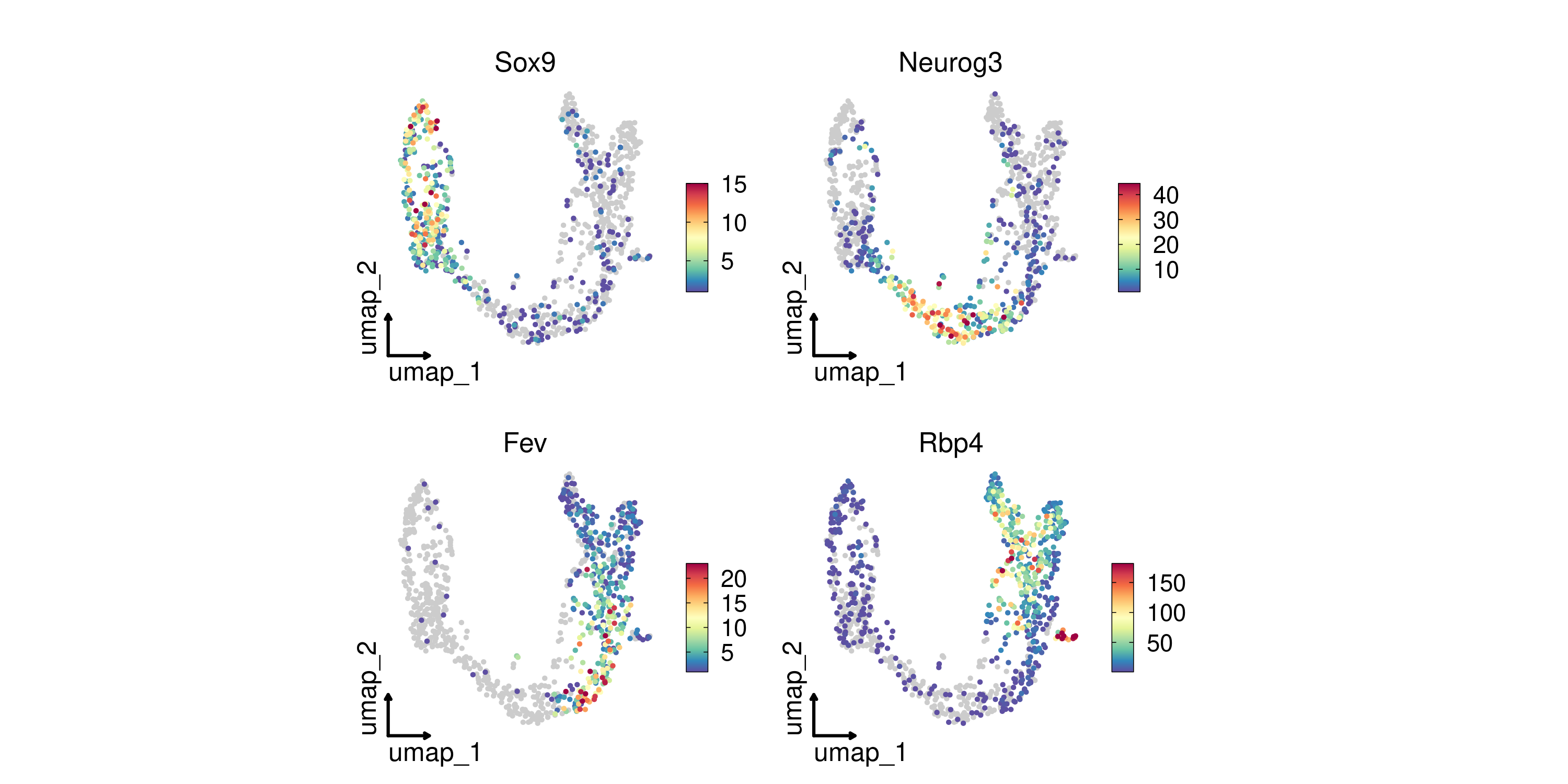
FeatureDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
features = c("Sox9", "Neurog3", "Fev", "Rbp4"),
reduction = "UMAP",
theme_use = "theme_blank"
)
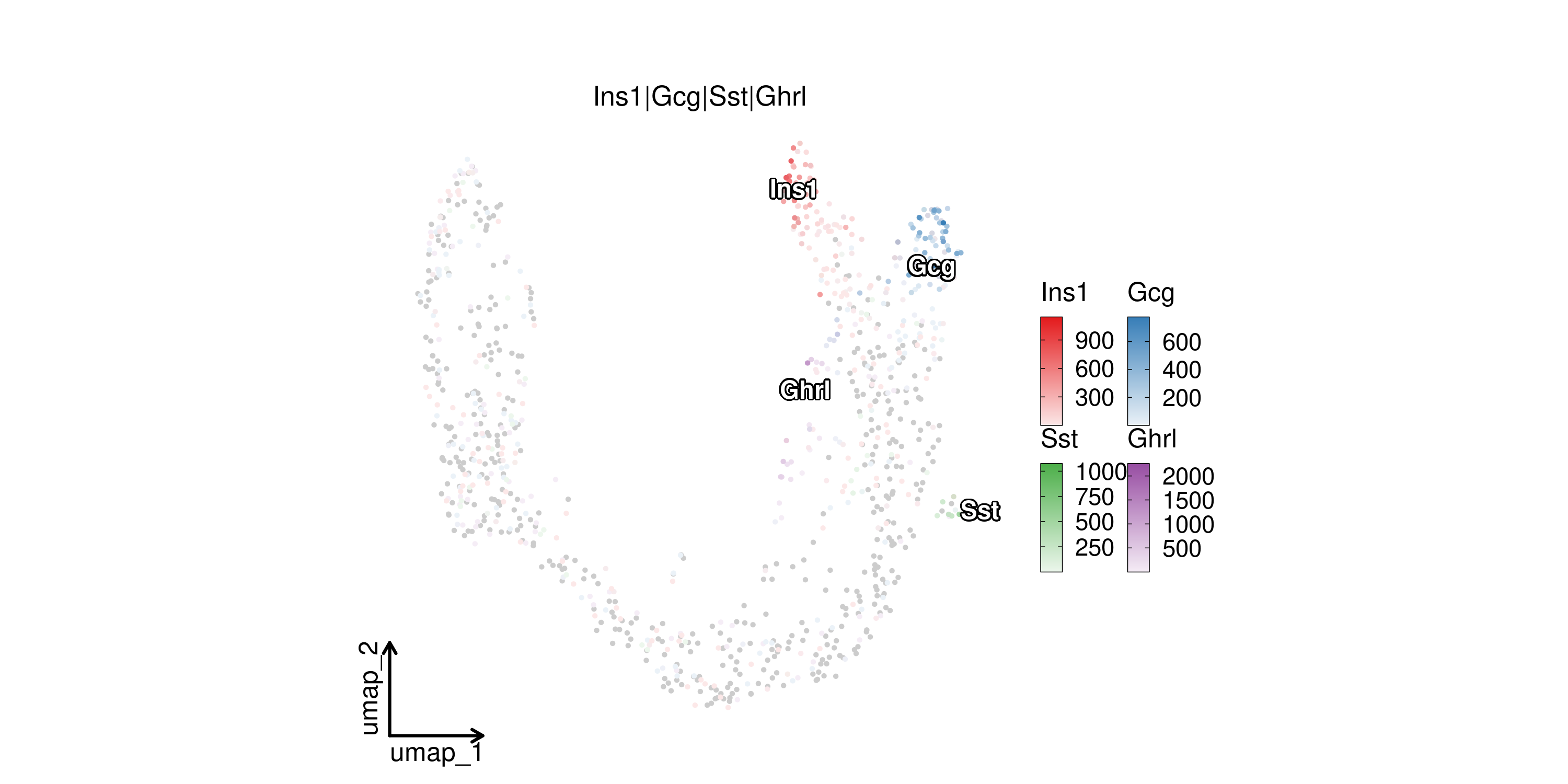
FeatureDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
features = c("Ins1", "Gcg", "Sst", "Ghrl"),
compare_features = TRUE,
label = TRUE,
label_insitu = TRUE,
reduction = "UMAP",
theme_use = "theme_blank"
)
ht <- GroupHeatmap(
pancreas_sub,
features = c(
"Sox9", "Anxa2", # Ductal
"Neurog3", "Hes6", # EPs
"Fev", "Neurod1", # Pre-endocrine
"Rbp4", "Pyy", # Endocrine
"Ins1", "Gcg", "Sst", "Ghrl" # Beta, Alpha, Delta, Epsilon
),
group.by = c("CellType", "SubCellType"),
heatmap_palette = "YlOrRd",
cell_annotation = c("Phase", "G2M_score", "Cdh2"),
cell_annotation_palette = c("Dark2", "Paired", "Paired"),
show_row_names = TRUE, row_names_side = "left",
add_dot = TRUE, add_reticle = TRUE
)
print(ht$plot)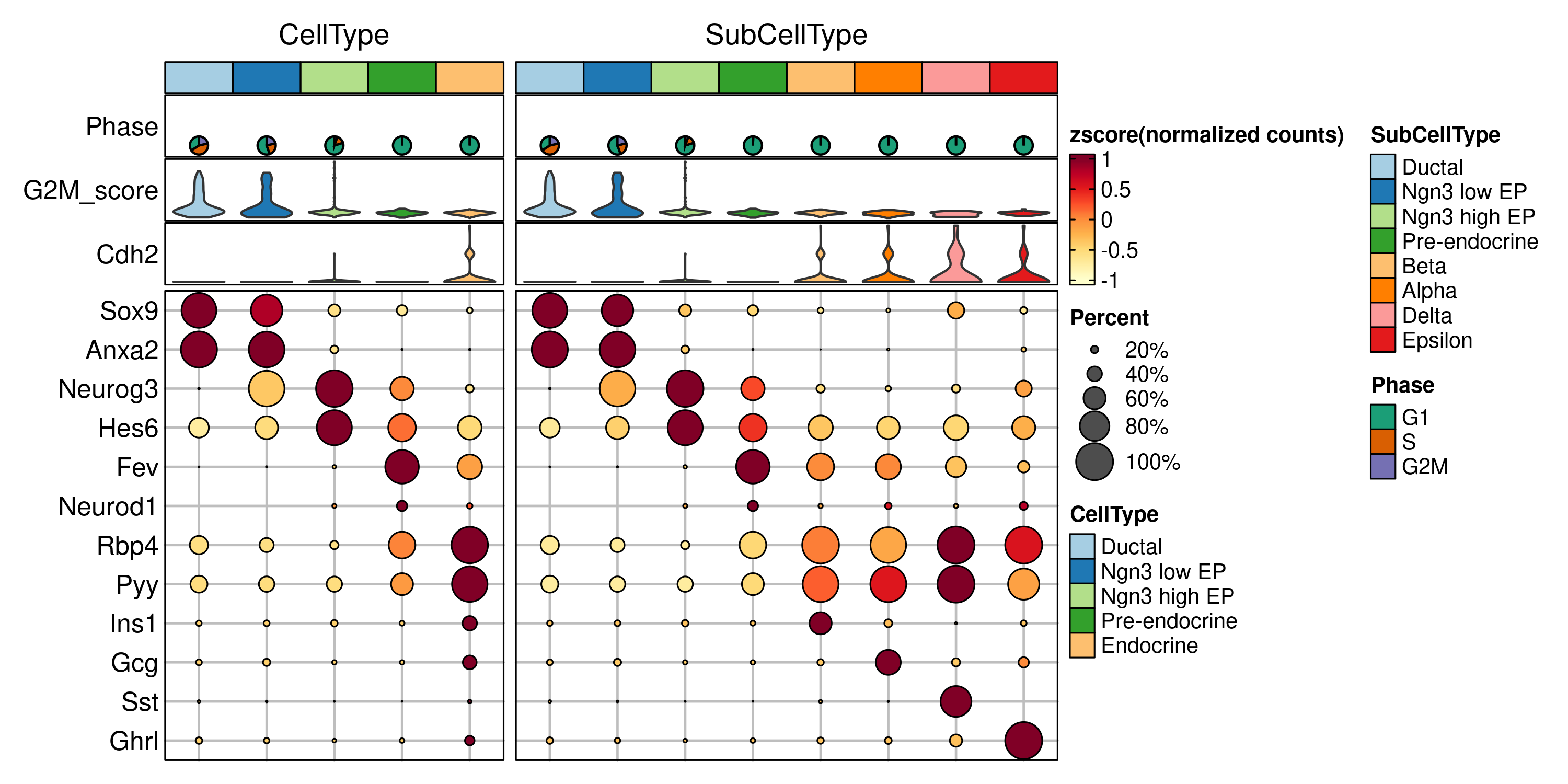
CellQC
pancreas_sub <- RunCellQC(pancreas_sub)
CellDimPlot(pancreas_sub, group.by = "CellQC", reduction = "UMAP")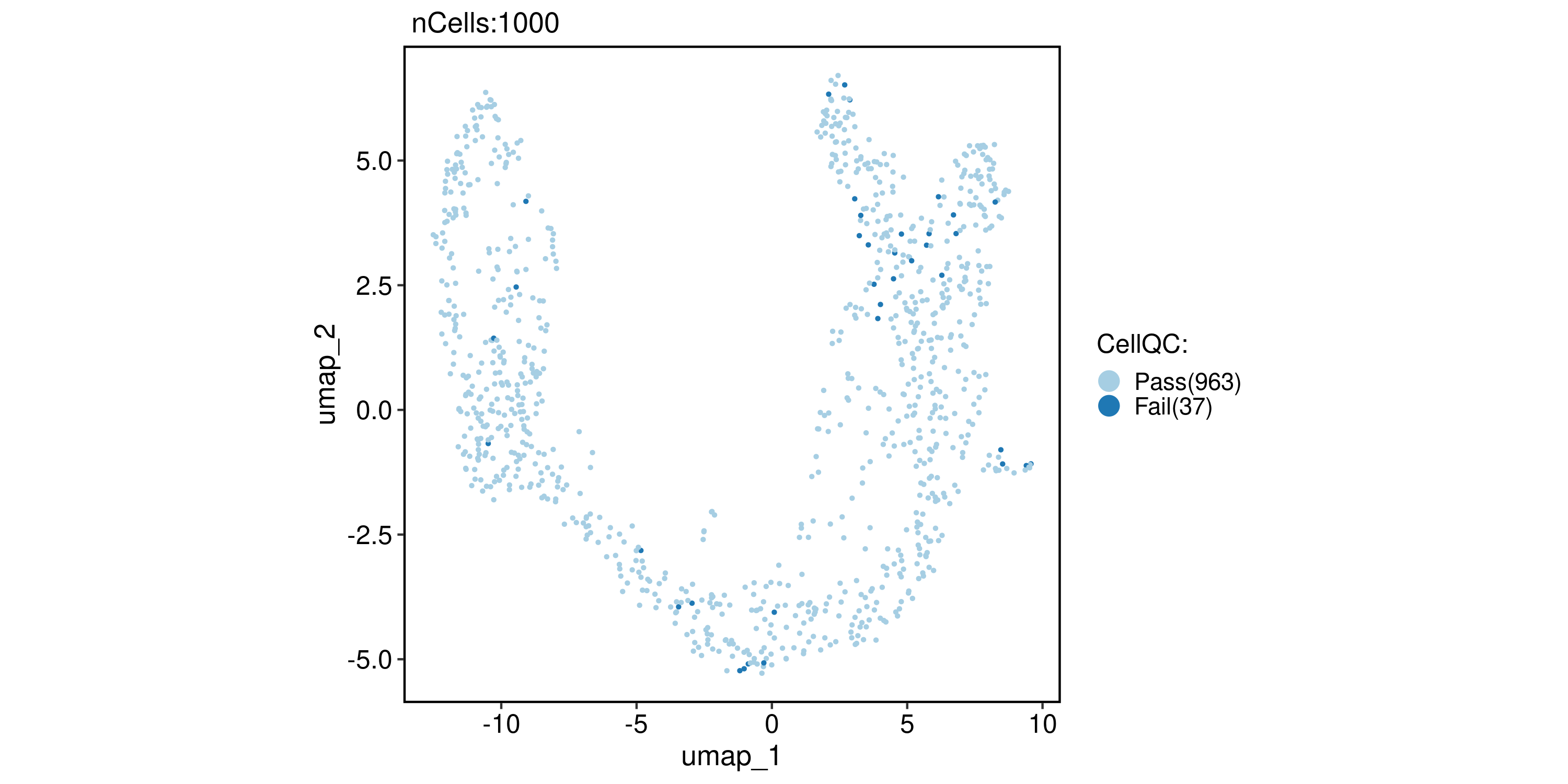
CellStatPlot(pancreas_sub, stat.by = "CellQC", group.by = "CellType", label = TRUE)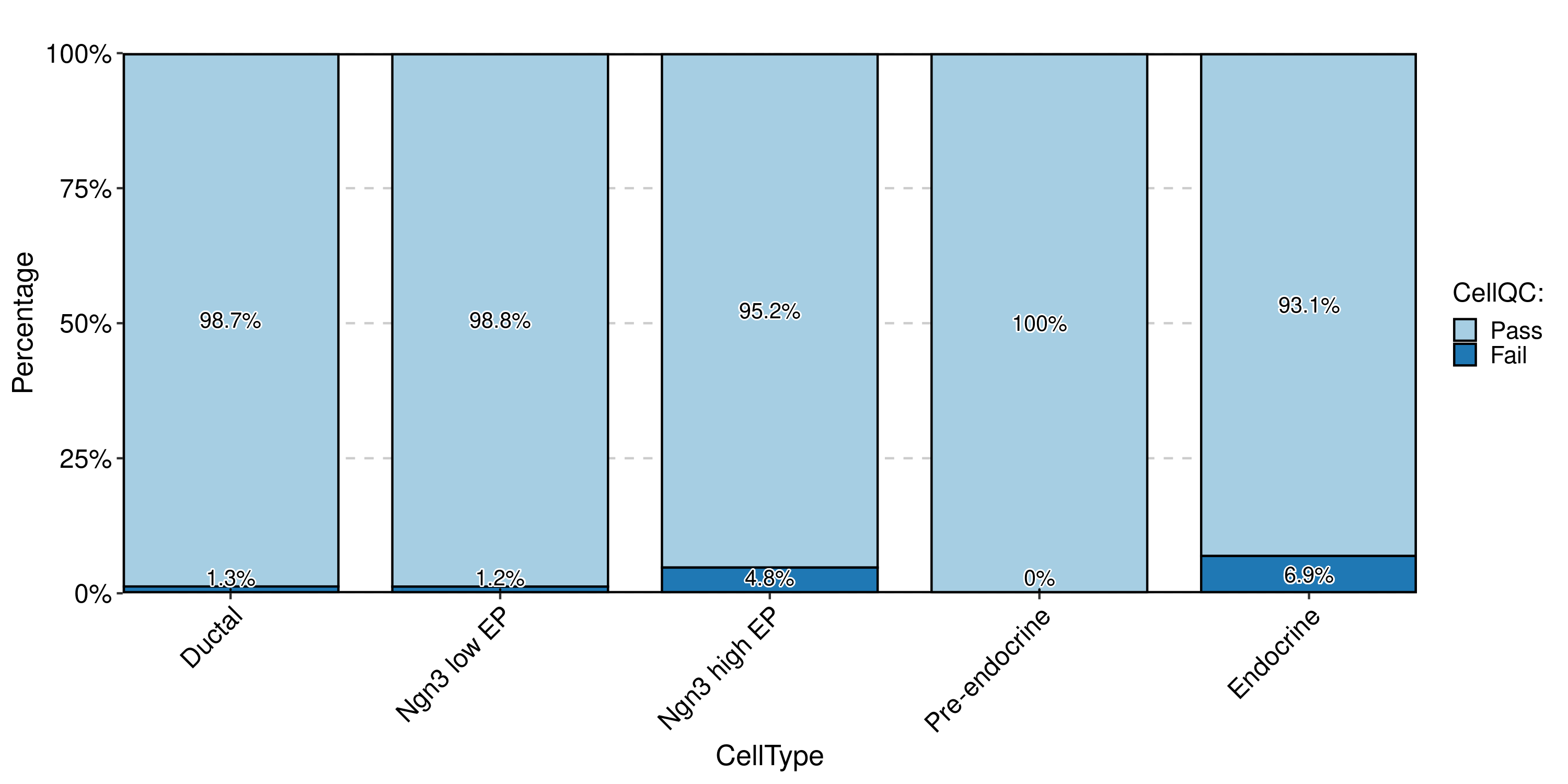
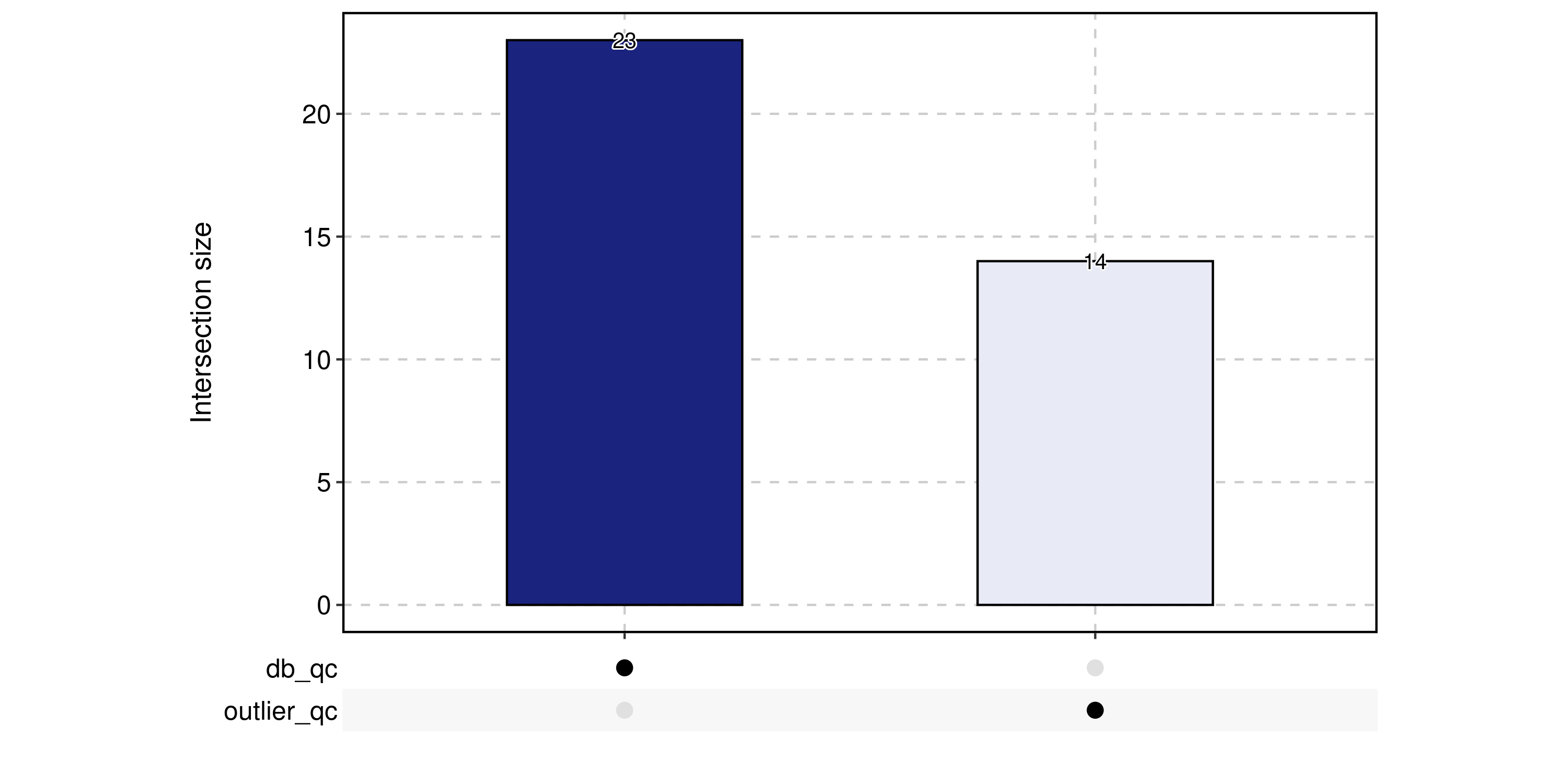
CellStatPlot(
pancreas_sub,
stat.by = c(
"db_qc", "outlier_qc",
"umi_qc", "gene_qc",
"mito_qc", "ribo_qc",
"ribo_mito_ratio_qc", "species_qc"
),
plot_type = "upset",
stat_level = "Fail"
)
Standard pipeline
pancreas_sub <- standard_scop(pancreas_sub)
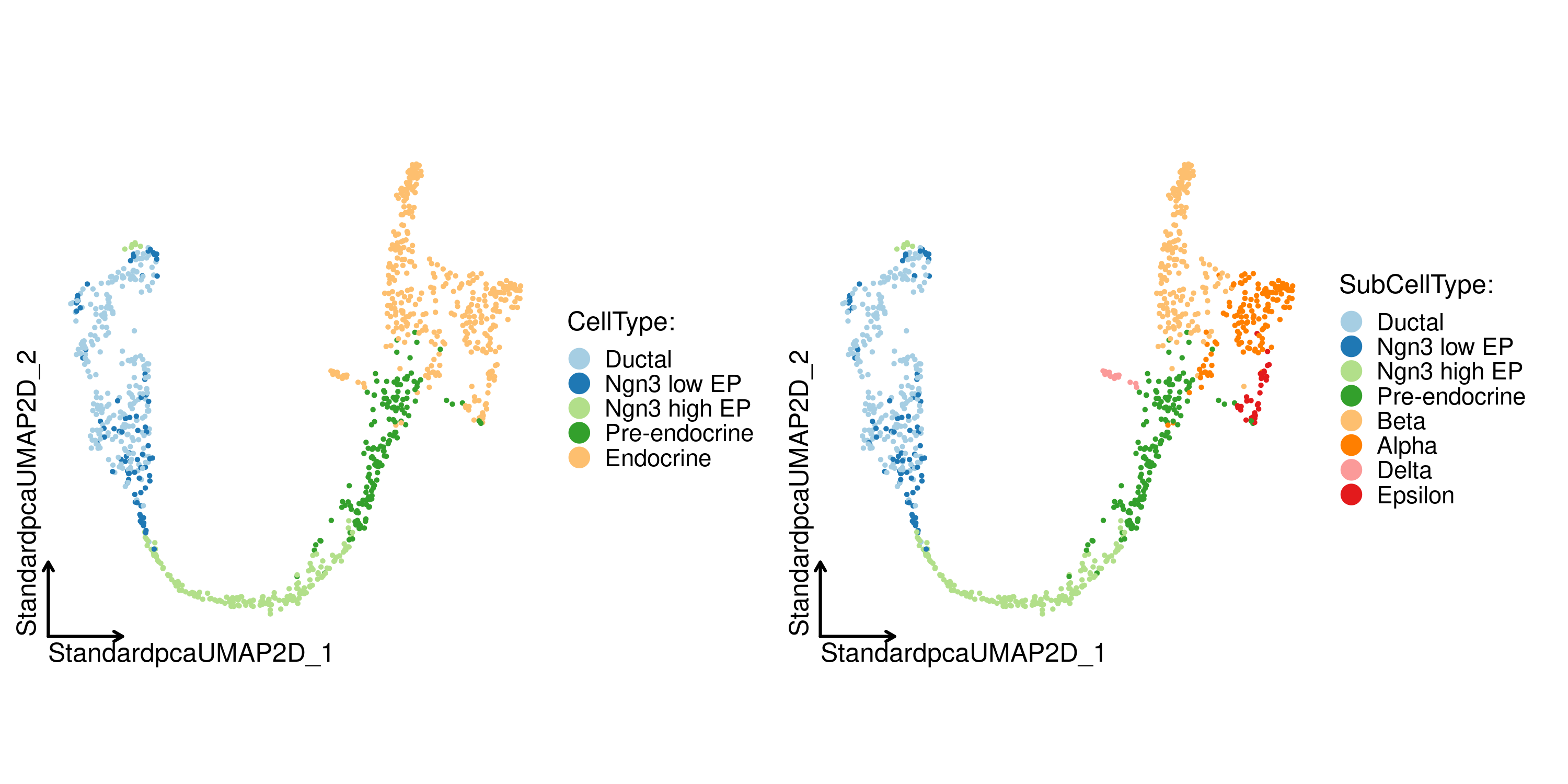
CellDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = c("CellType", "SubCellType"),
reduction = "StandardUMAP2D",
theme_use = "theme_blank"
)
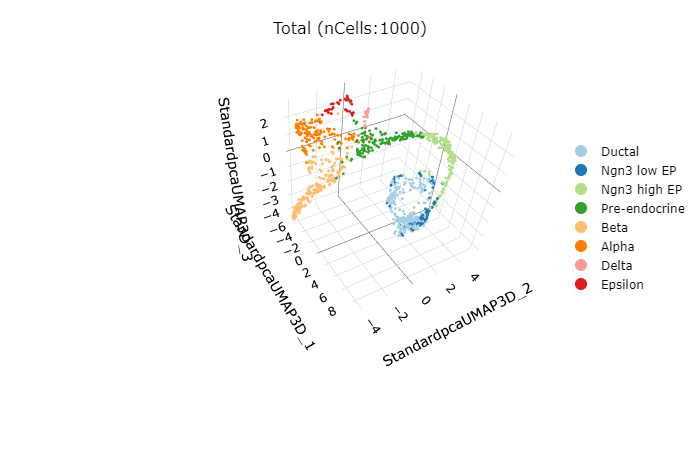
CellDimPlot3D(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "SubCellType"
)
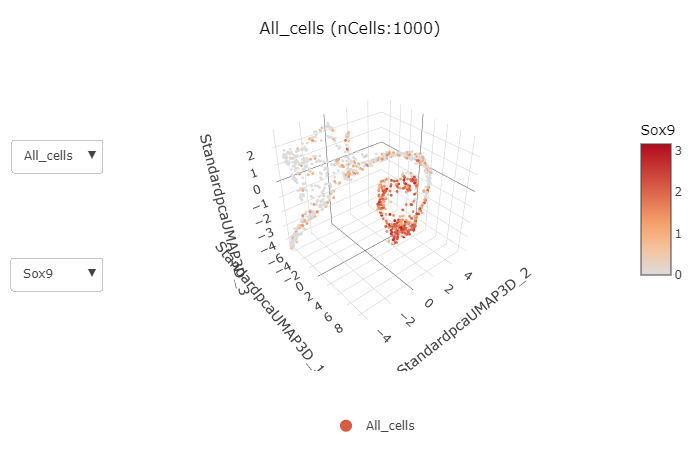
FeatureDimPlot3D(
pancreas_sub,
features = c("Sox9", "Neurog3", "Fev", "Rbp4")
)
Integration pipeline
Example data for integration is a subsetted version of panc8(eight human pancreas datasets)
data("panc8_sub")
panc8_sub <- integration_scop(
srt_merge = panc8_sub,
batch = "tech",
integration_method = "Seurat"
)
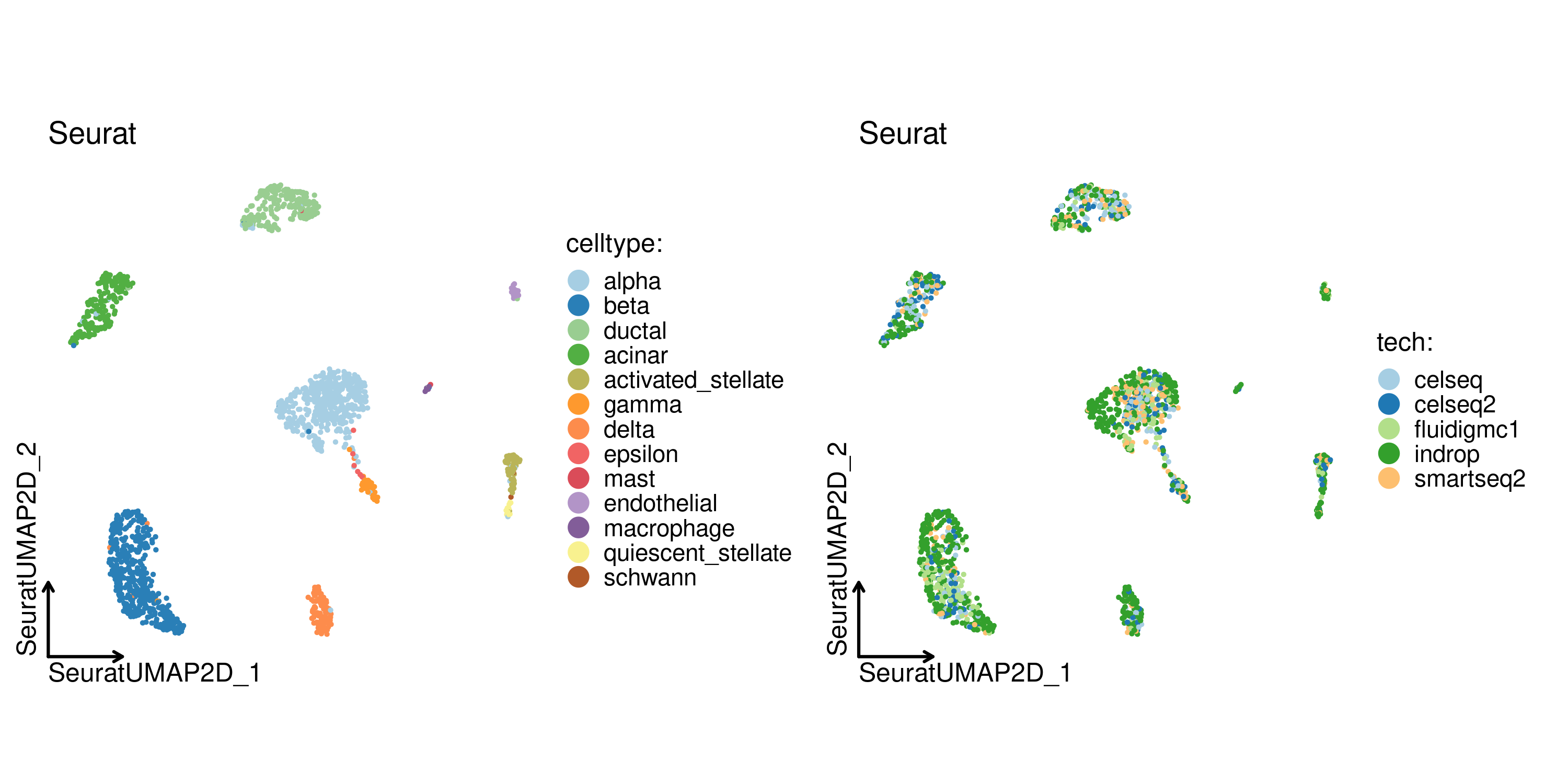
CellDimPlot(
panc8_sub,
group.by = c("celltype", "tech"),
reduction = "SeuratUMAP2D",
title = "Seurat",
theme_use = "theme_blank"
)
Cell projection between single-cell datasets
genenames <- make.unique(
thisutils::capitalize(
rownames(panc8_sub[["RNA"]]
),
force_tolower = TRUE)
)
names(genenames) <- rownames(panc8_sub)
panc8_rename <- RenameFeatures(
panc8_sub,
newnames = genenames,
assays = "RNA"
)
srt_query <- RunKNNMap(
srt_query = pancreas_sub,
srt_ref = panc8_rename,
ref_umap = "SeuratUMAP2D")
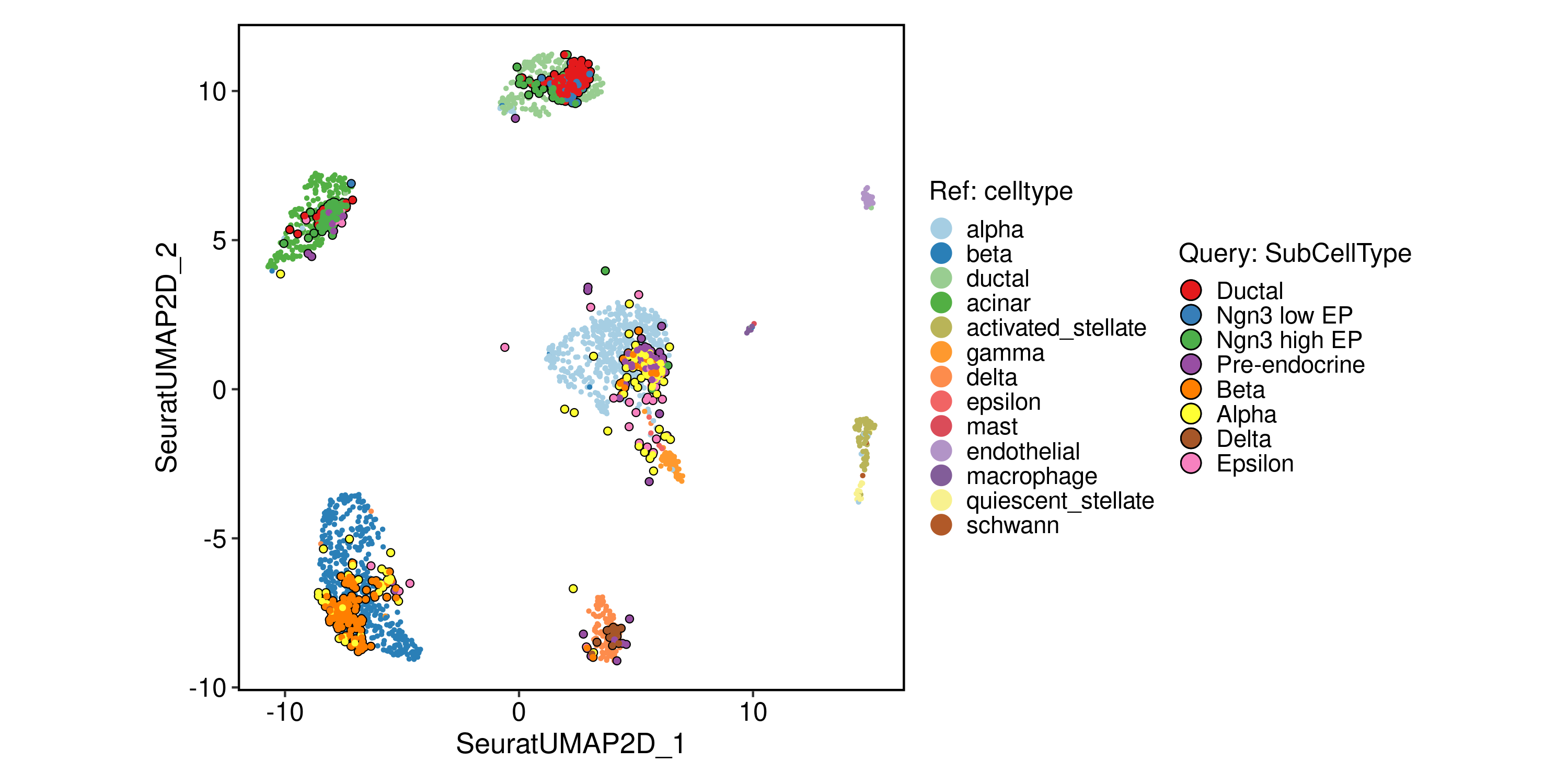
ProjectionPlot(
srt_query = srt_query,
srt_ref = panc8_rename,
query_group = "SubCellType",
ref_group = "celltype"
)
Cell annotation using bulk RNA-seq datasets
data("ref_scMCA")
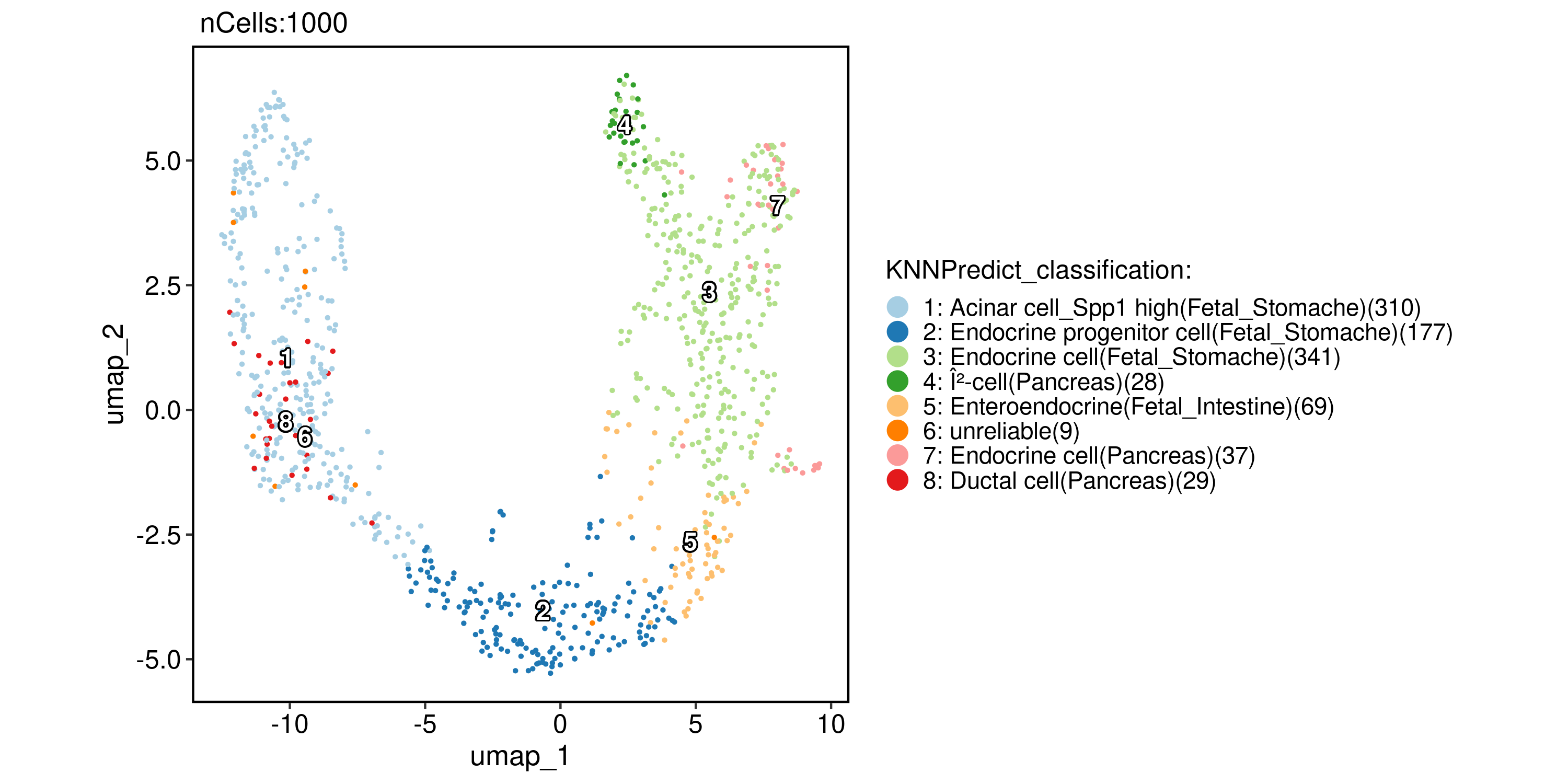
pancreas_sub <- RunKNNPredict(
srt_query = pancreas_sub,
bulk_ref = ref_scMCA,
filter_lowfreq = 20
)
CellDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "KNNPredict_classification",
reduction = "UMAP",
label = TRUE
)
Cell annotation using single-cell datasets
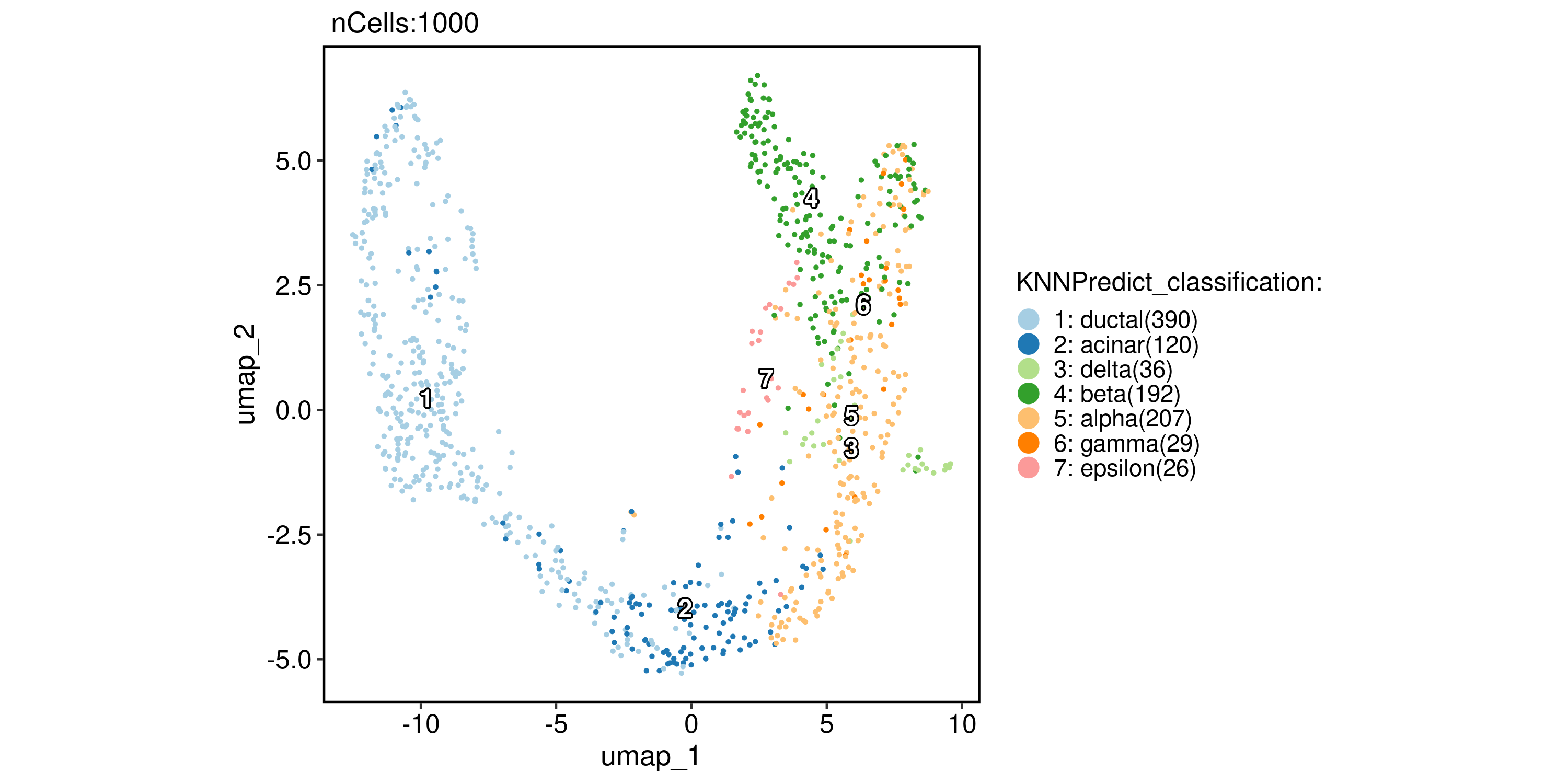
pancreas_sub <- RunKNNPredict(
srt_query = pancreas_sub,
srt_ref = panc8_rename,
ref_group = "celltype",
filter_lowfreq = 20
)
CellDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "KNNPredict_classification",
reduction = "UMAP",
label = TRUE
)
ht <- CellCorHeatmap(
srt_query = pancreas_sub,
srt_ref = panc8_rename,
query_group = "SubCellType",
ref_group = "celltype",
nlabel = 3,
label_by = "row",
show_row_names = TRUE,
show_column_names = TRUE
)
print(ht$plot)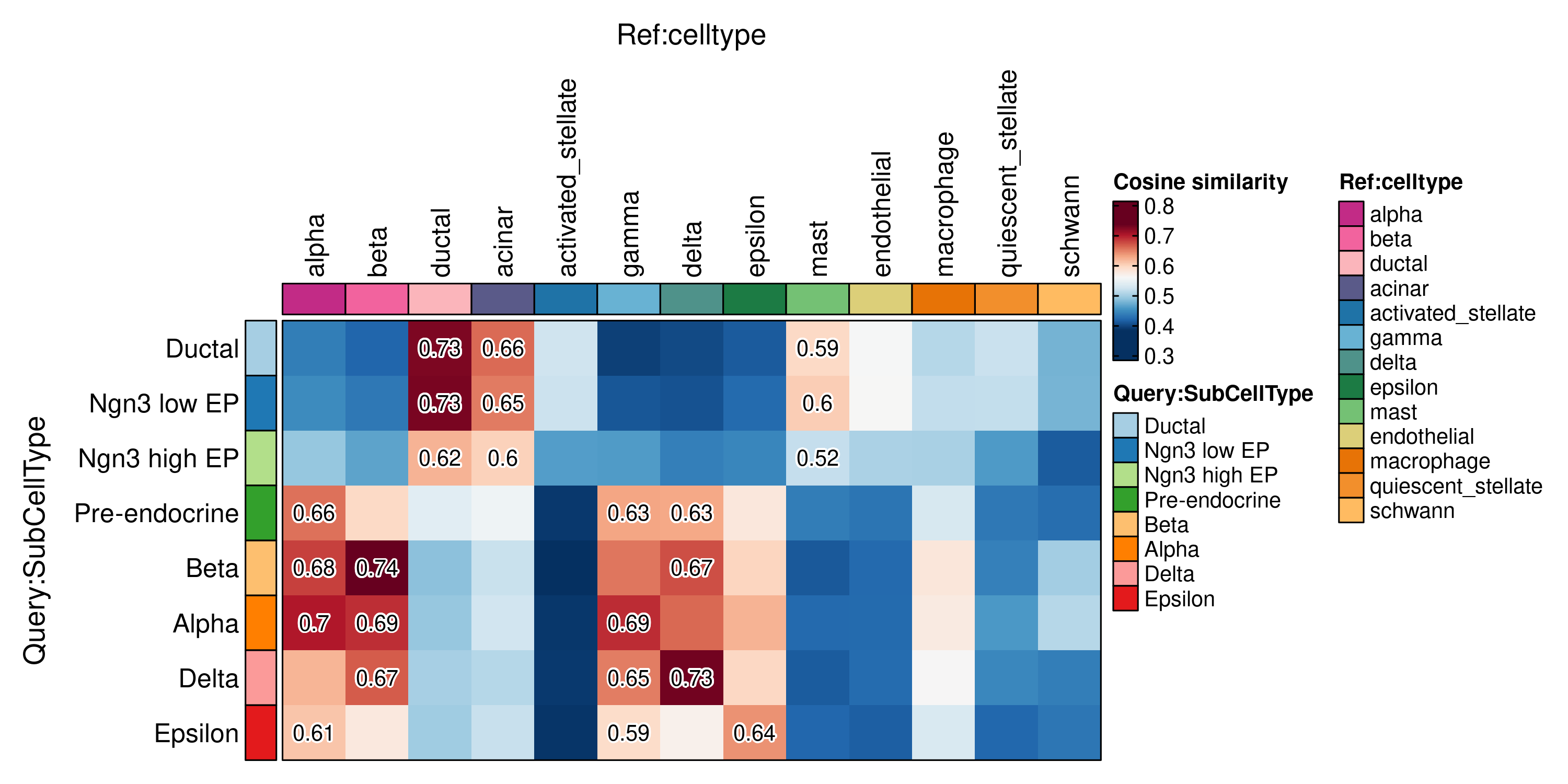
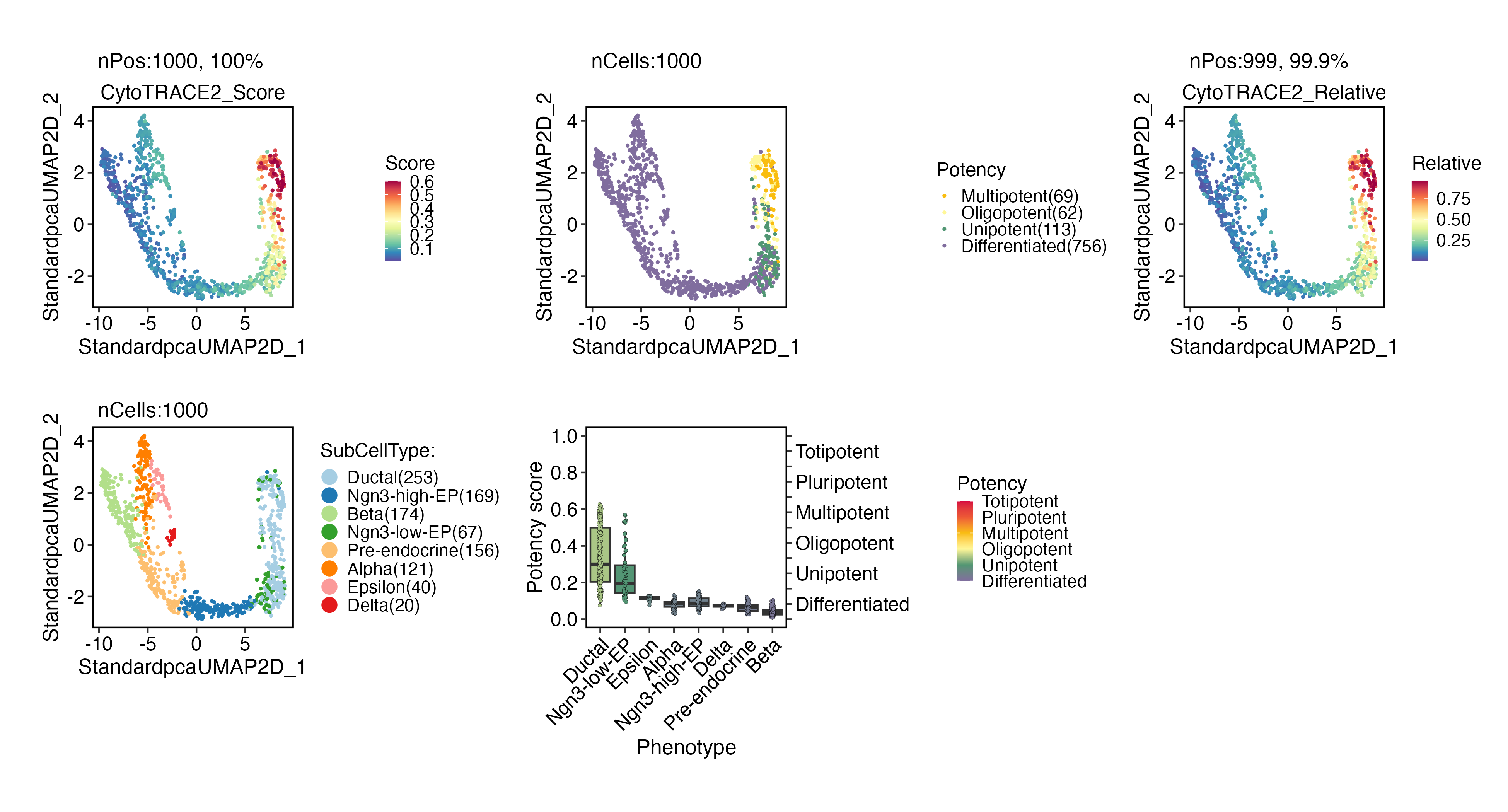
Cellular potency
CytoTRACE 2
pancreas_sub <- RunCytoTRACE(
pancreas_sub,
species = "mouse"
)
CytoTRACEPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "SubCellType"
)
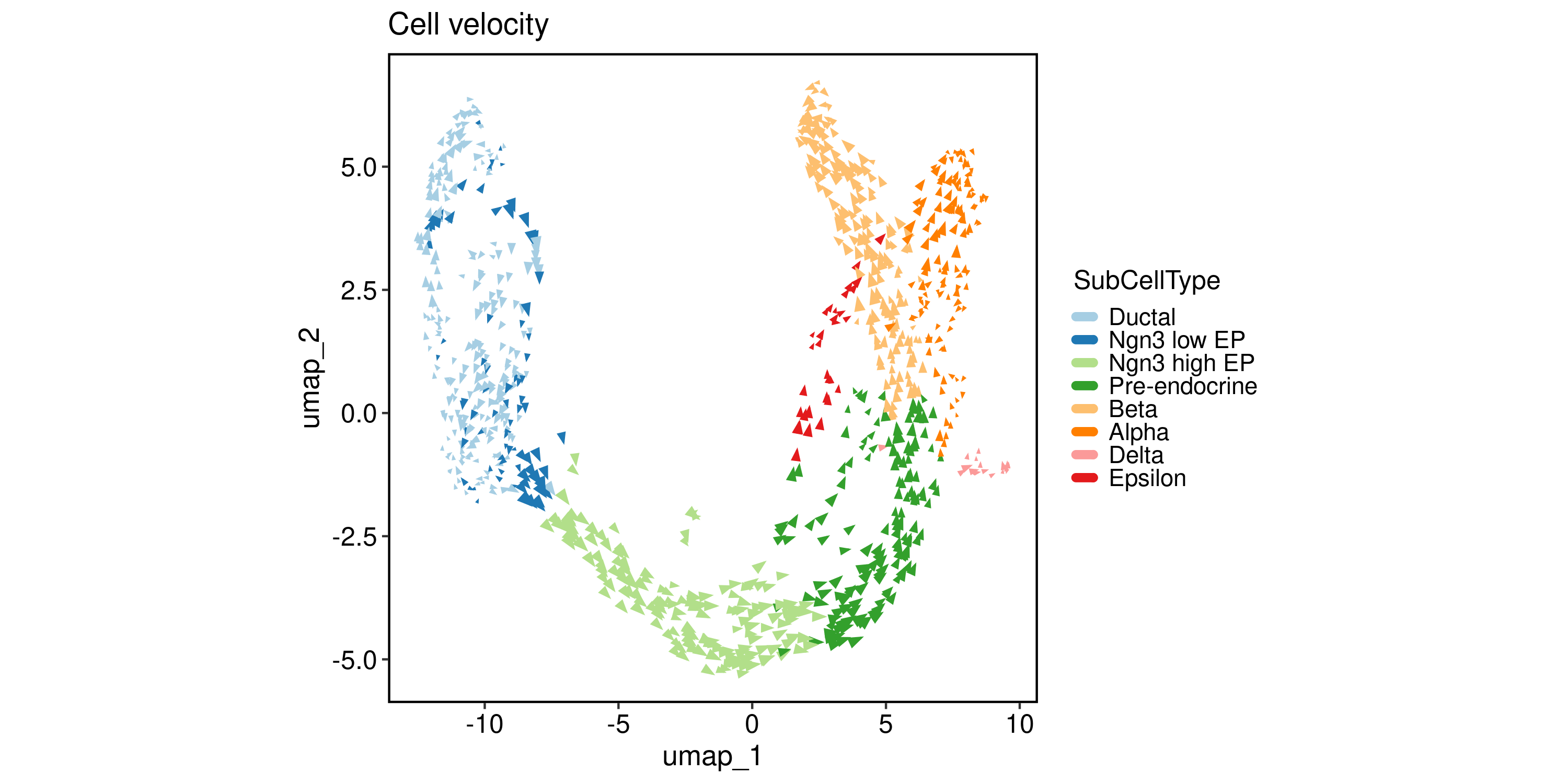
Velocity analysis
To estimate RNA velocity, both “spliced” and “unspliced” assays in Seurat object. You can generate these matrices using velocyto, bustools, or alevin.
SCVELO
pancreas_sub <- RunSCVELO(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "SubCellType",
linear_reduction = "PCA",
nonlinear_reduction = "UMAP"
)
VelocityPlot(
pancreas_sub,
reduction = "UMAP",
group_by = "SubCellType"
)
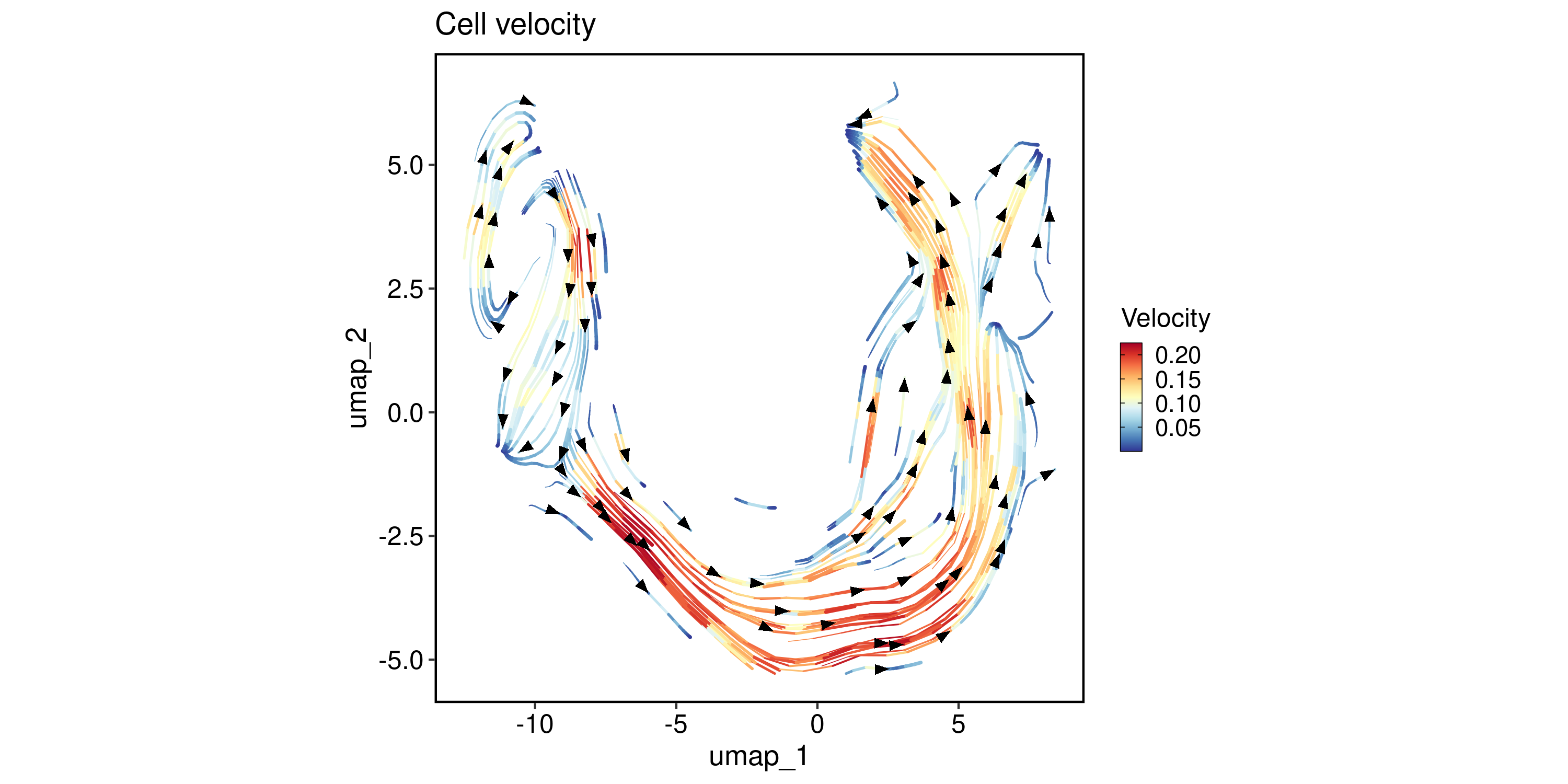
VelocityPlot(
pancreas_sub,
reduction = "UMAP",
plot_type = "stream"
)
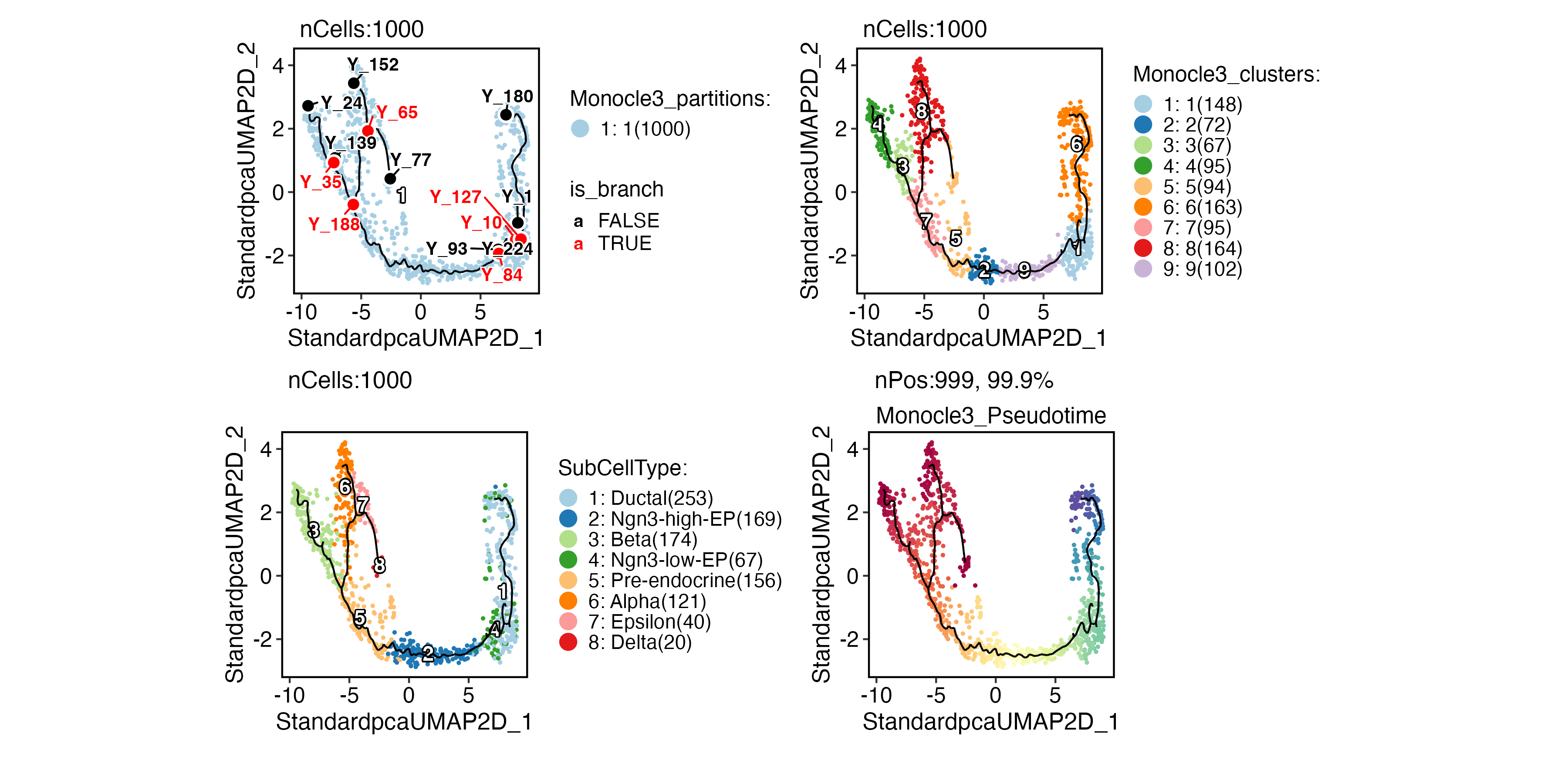
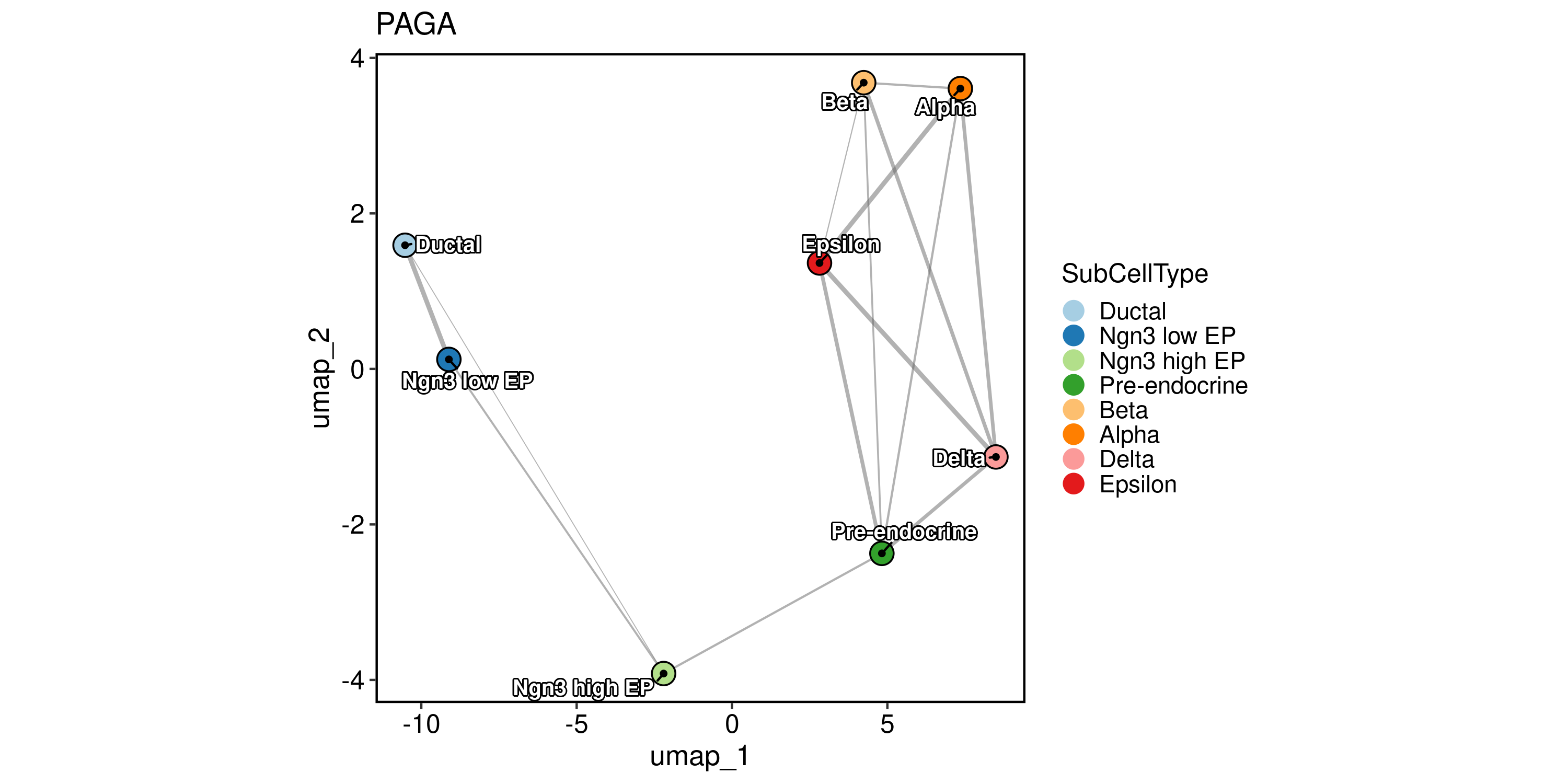
Trajectory inference
PAGA analysis
PrepareEnv()
pancreas_sub <- RunPAGA(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "SubCellType",
linear_reduction = "PCA",
nonlinear_reduction = "UMAP"
)
PAGAPlot(
pancreas_sub,
reduction = "UMAP",
label = TRUE,
label_insitu = TRUE,
label_repel = TRUE
)
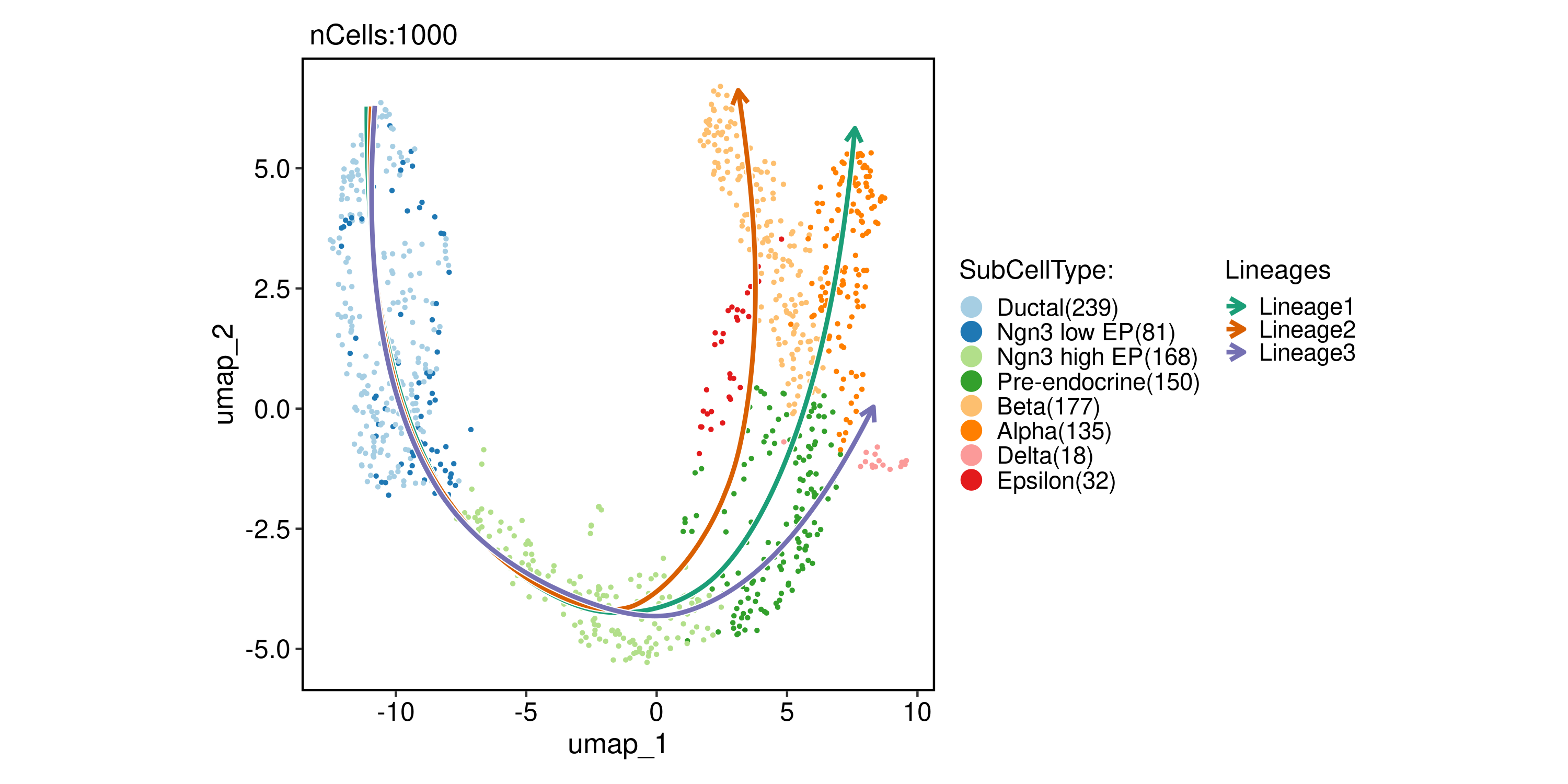
Slingshot
pancreas_sub <- RunSlingshot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "SubCellType",
reduction = "UMAP"
)
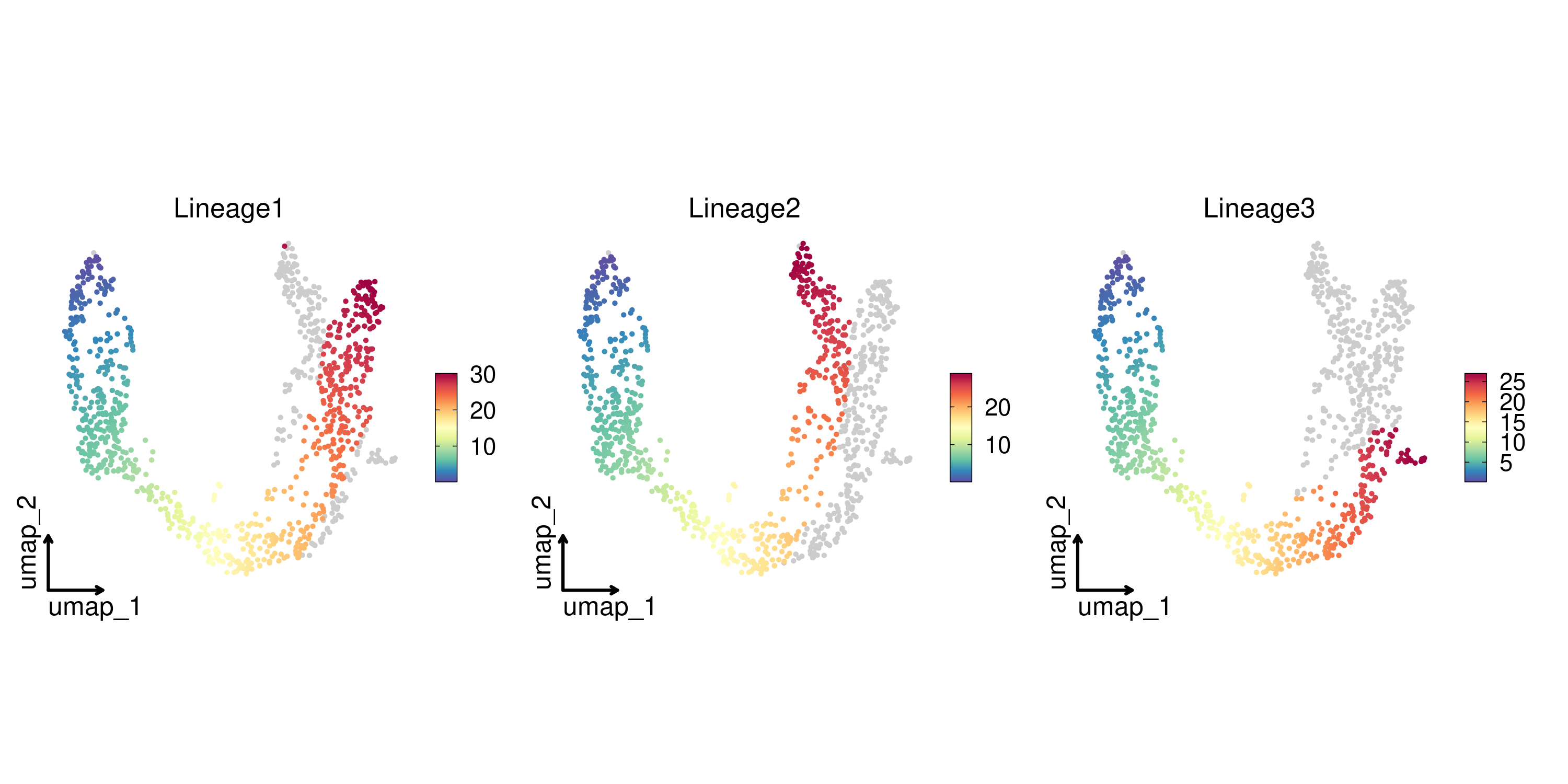
FeatureDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
features = paste0("Lineage", 1:3),
reduction = "UMAP",
theme_use = "theme_blank"
)
Dynamic features
pancreas_sub <- RunDynamicFeatures(
pancreas_sub,
lineages = c("Lineage1", "Lineage2"),
n_candidates = 200
)
ht <- DynamicHeatmap(
pancreas_sub,
lineages = c("Lineage1", "Lineage2"),
use_fitted = TRUE,
n_split = 6,
reverse_ht = "Lineage1",
species = "Mus_musculus",
db = "GO_BP",
anno_terms = TRUE,
anno_keys = TRUE,
anno_features = TRUE,
heatmap_palette = "viridis",
cell_annotation = "SubCellType",
separate_annotation = list(
"SubCellType", c("Nnat", "Irx1")
),
separate_annotation_palette = c("Paired", "Set1"),
feature_annotation = c("TF", "CSPA"),
feature_annotation_palcolor = list(
c("gold", "steelblue"), c("forestgreen")
),
pseudotime_label = 25,
pseudotime_label_color = "red",
height = 5,
width = 2
)
print(ht$plot)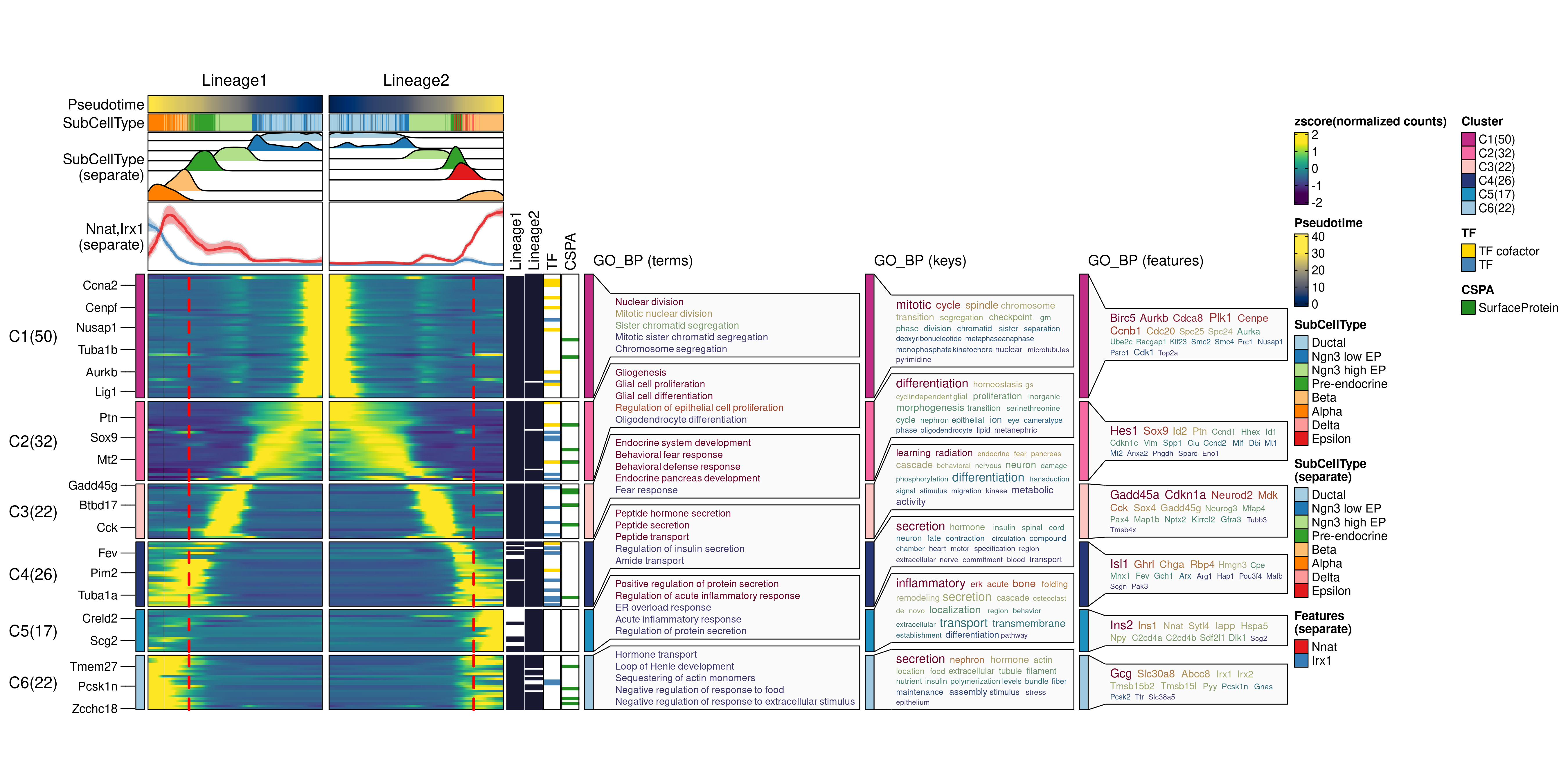
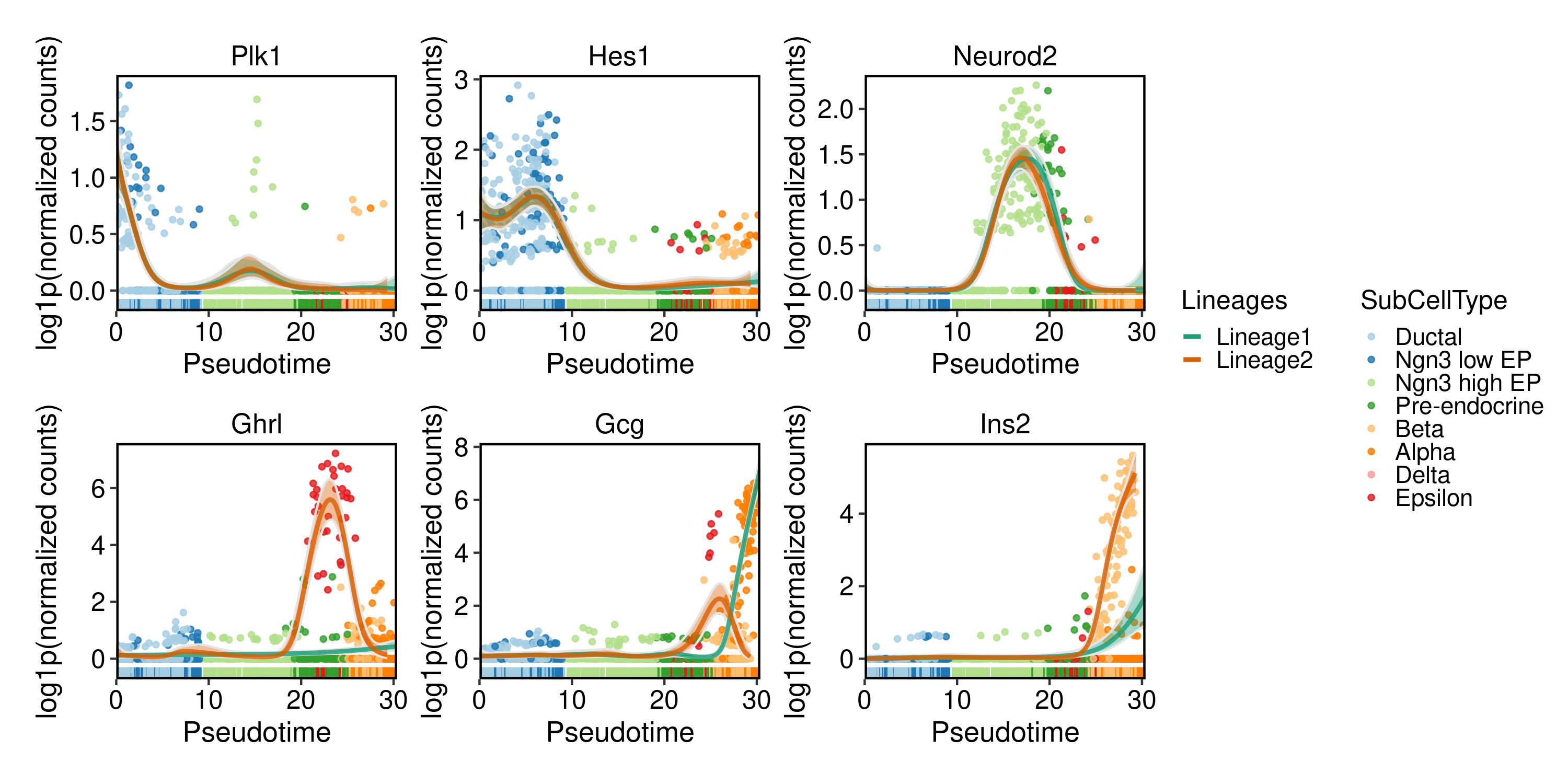
DynamicPlot(
pancreas_sub,
lineages = c("Lineage1", "Lineage2"),
group.by = "SubCellType",
features = c(
"Plk1", "Hes1", "Neurod2", "Ghrl", "Gcg", "Ins2"
),
compare_lineages = TRUE,
compare_features = FALSE
)
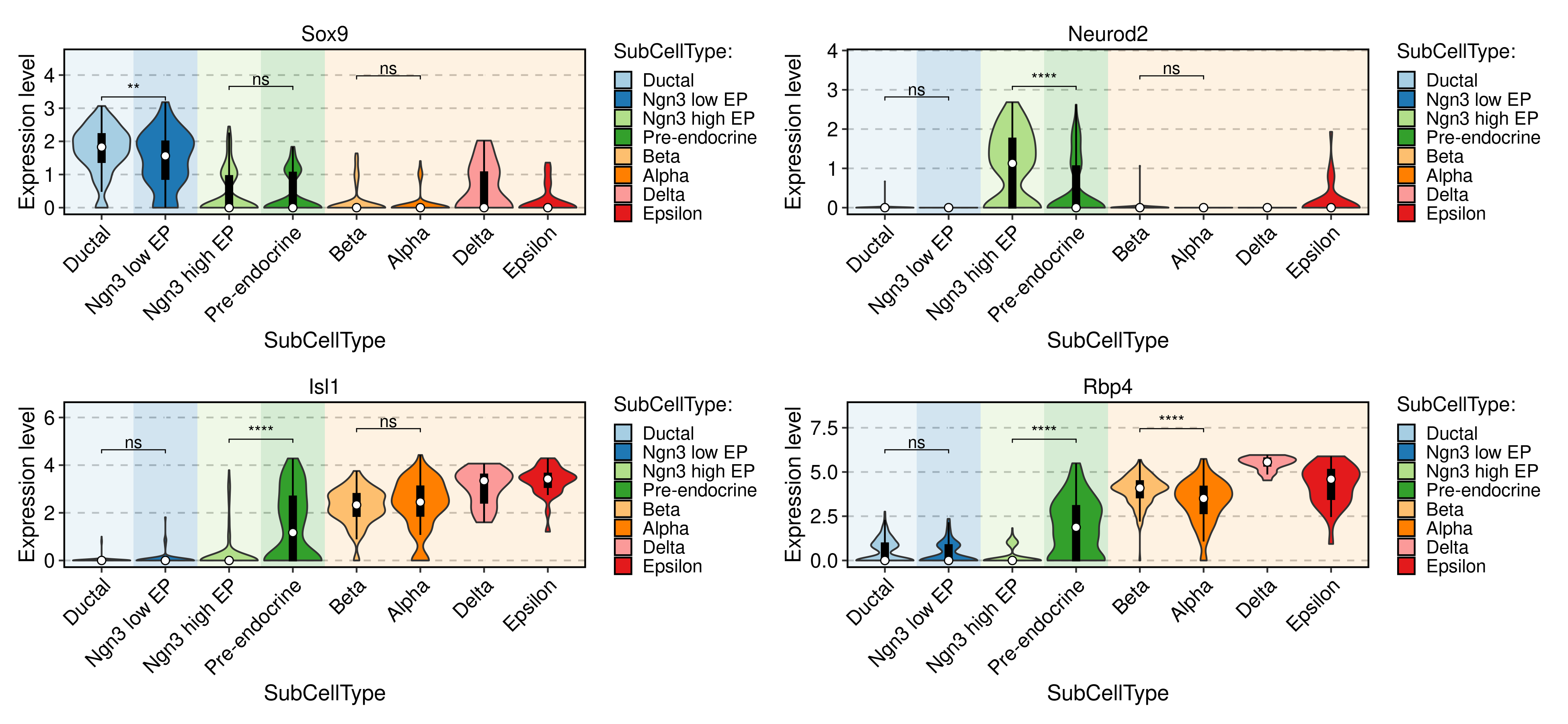
FeatureStatPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "SubCellType",
bg.by = "CellType",
stat.by = c("Sox9", "Neurod2", "Isl1", "Rbp4"),
add_box = TRUE,
comparisons = list(
c("Ductal", "Ngn3 low EP"),
c("Ngn3 high EP", "Pre-endocrine"),
c("Alpha", "Beta")
)
)
Differential expression analysis
pancreas_sub <- RunDEtest(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType",
fc.threshold = 1,
only.pos = FALSE
)
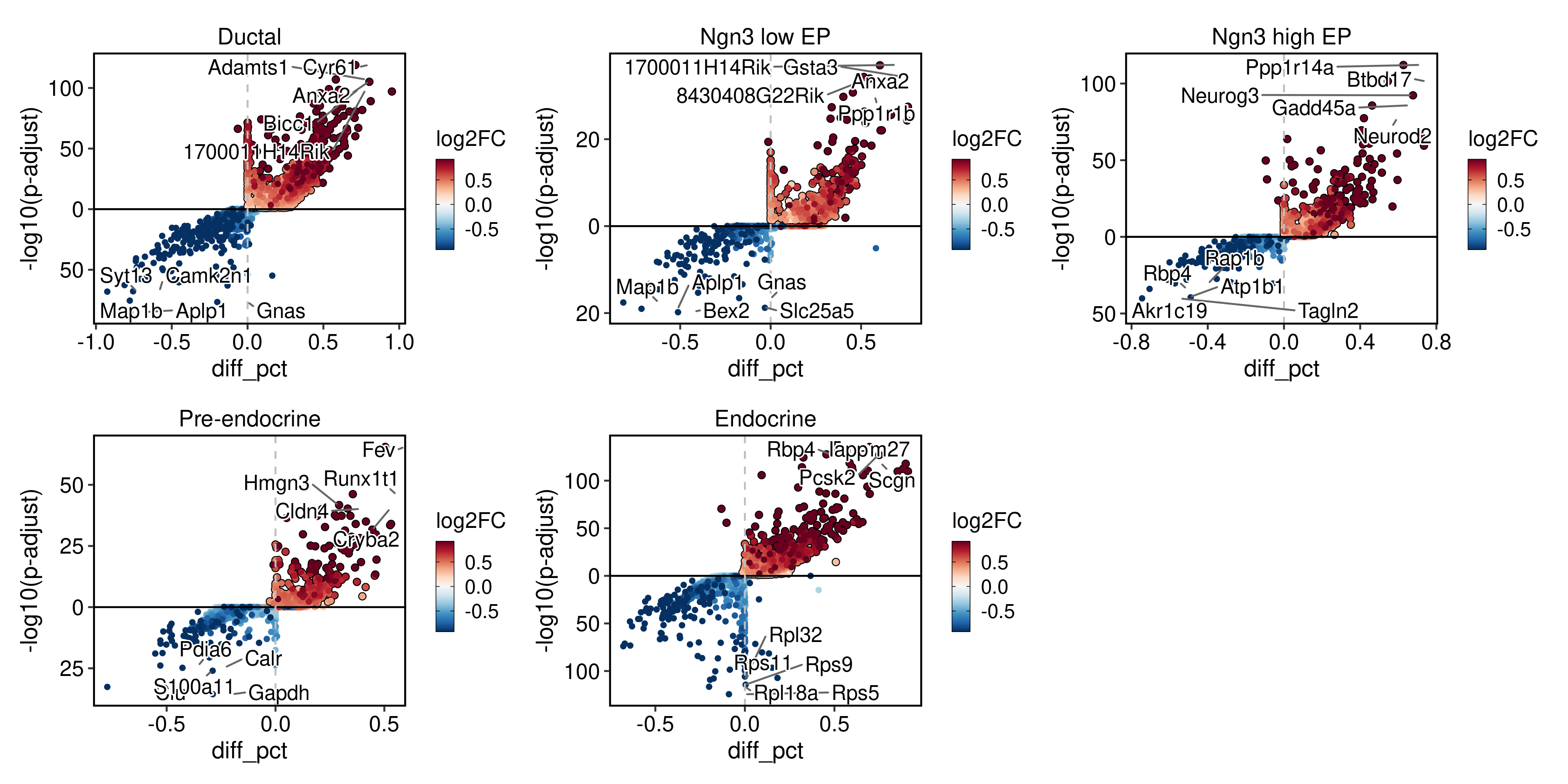
VolcanoPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType"
)
DEGs <- pancreas_sub@tools$DEtest_CellType$AllMarkers_wilcox
DEGs <- DEGs[with(DEGs, avg_log2FC > 1 & p_val_adj < 0.05), ]
# Annotate features with transcription factors and surface proteins
pancreas_sub <- AnnotateFeatures(
pancreas_sub,
species = "Mus_musculus",
db = c("TF", "CSPA")
)
ht <- FeatureHeatmap(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "CellType",
features = DEGs$gene,
feature_split = DEGs$group1,
species = "Mus_musculus",
db = c("GO_BP", "KEGG", "WikiPathway"),
anno_terms = TRUE,
feature_annotation = c("TF", "CSPA"),
feature_annotation_palcolor = list(
c("gold", "steelblue"), c("forestgreen")
),
height = 5, width = 4
)
print(ht$plot)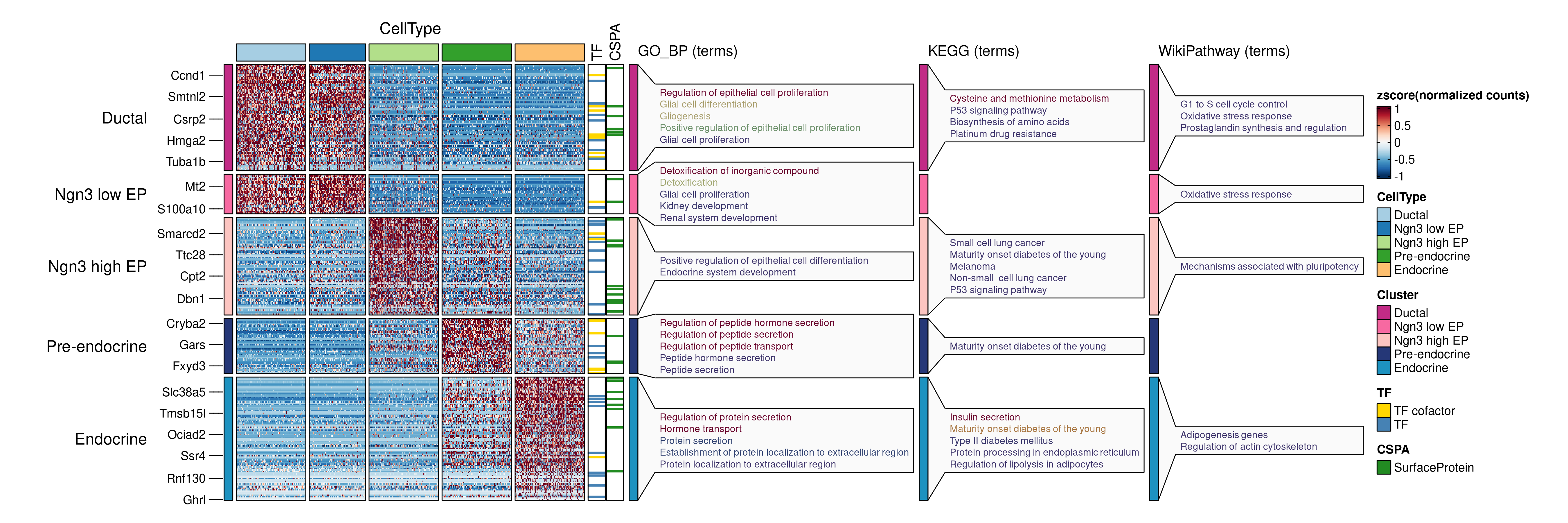
Enrichment analysis(over-representation)
pancreas_sub <- RunEnrichment(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType",
db = "GO_BP",
species = "Mus_musculus",
DE_threshold = "avg_log2FC > log2(1.5) & p_val_adj < 0.05"
)
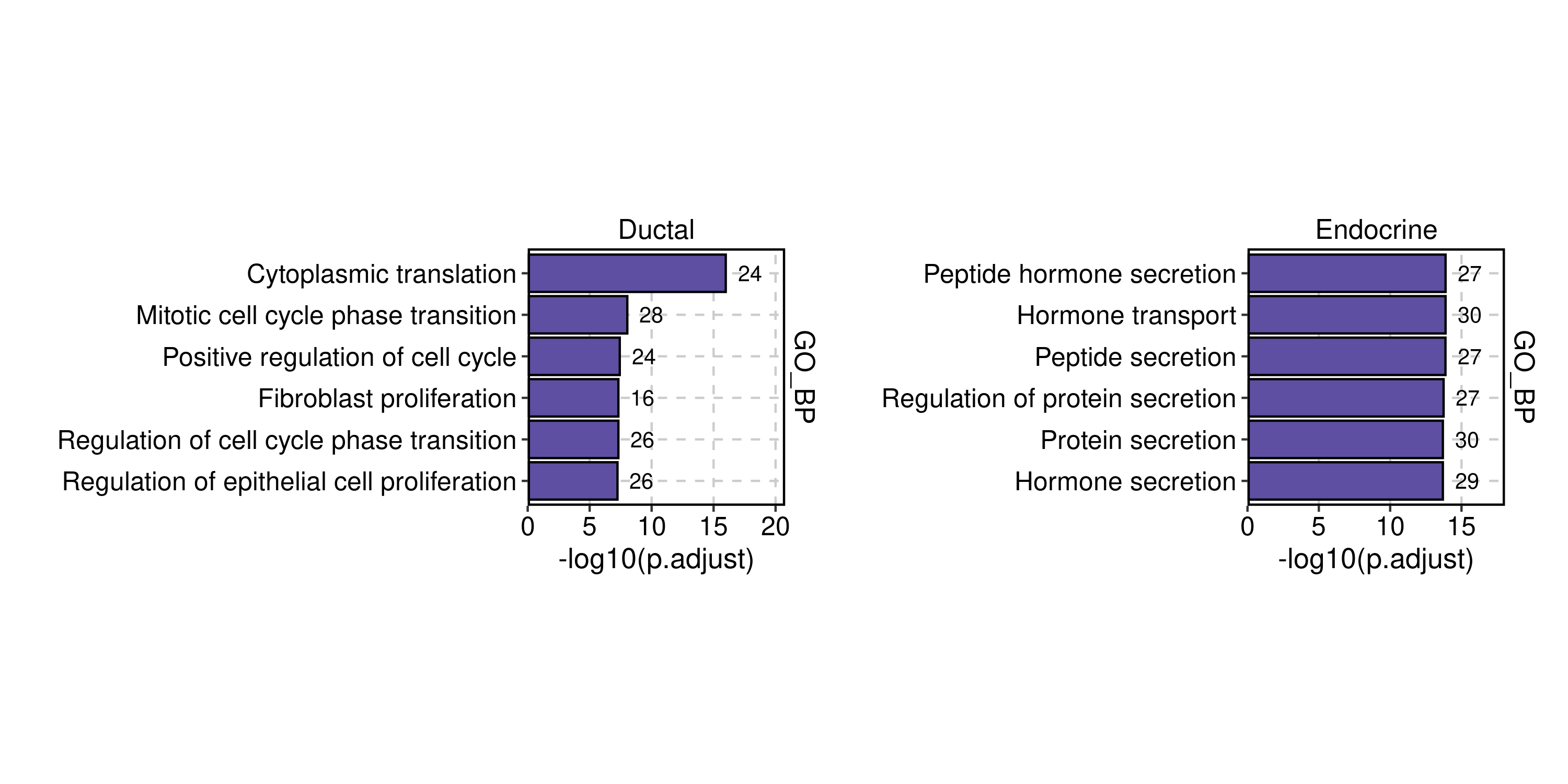
EnrichmentPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType",
group_use = c("Ductal", "Endocrine"),
plot_type = "bar"
)
EnrichmentPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType",
group_use = c("Ductal", "Endocrine"),
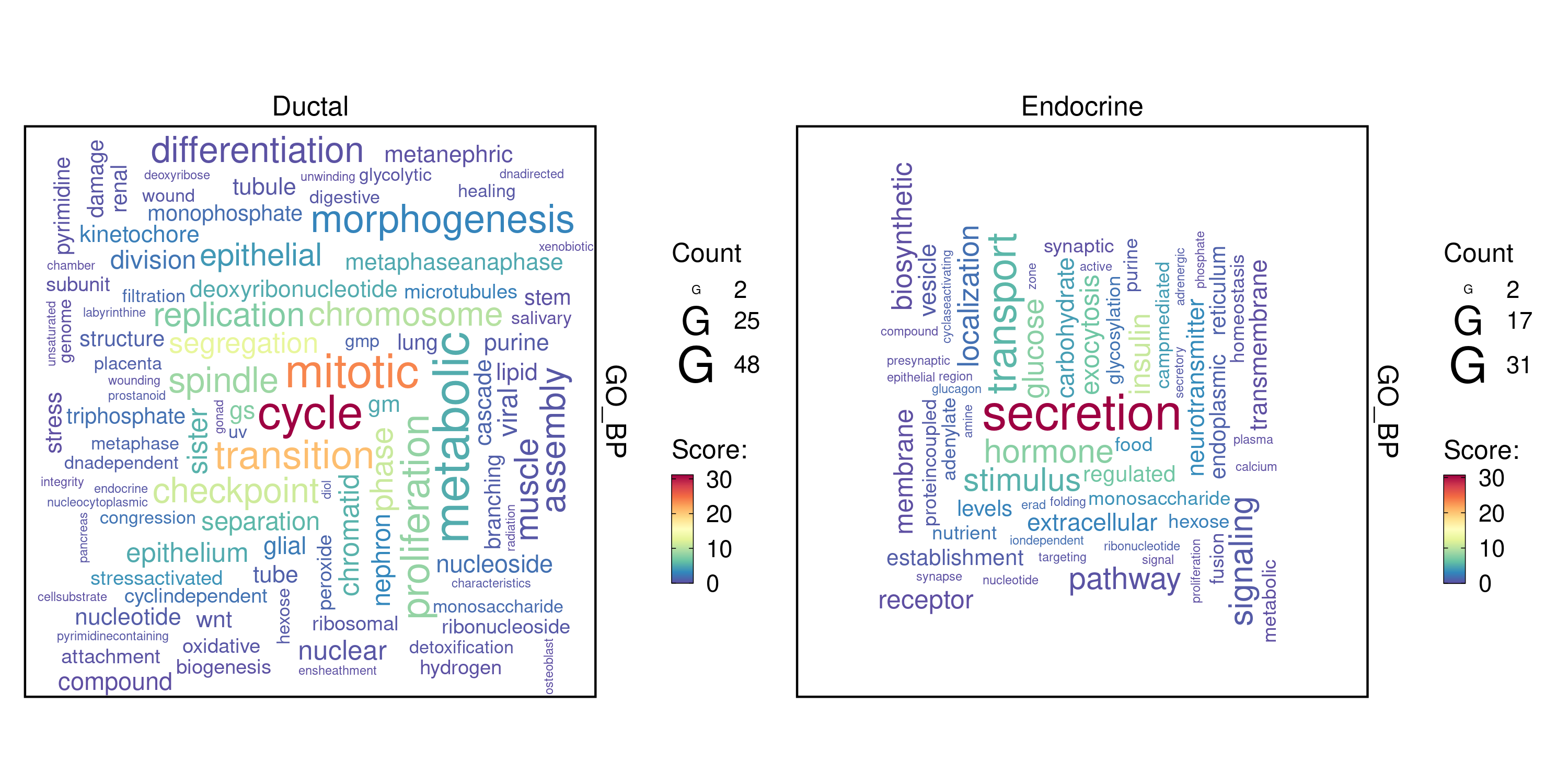
plot_type = "wordcloud"
)
EnrichmentPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType",
group_use = c("Ductal", "Endocrine"),
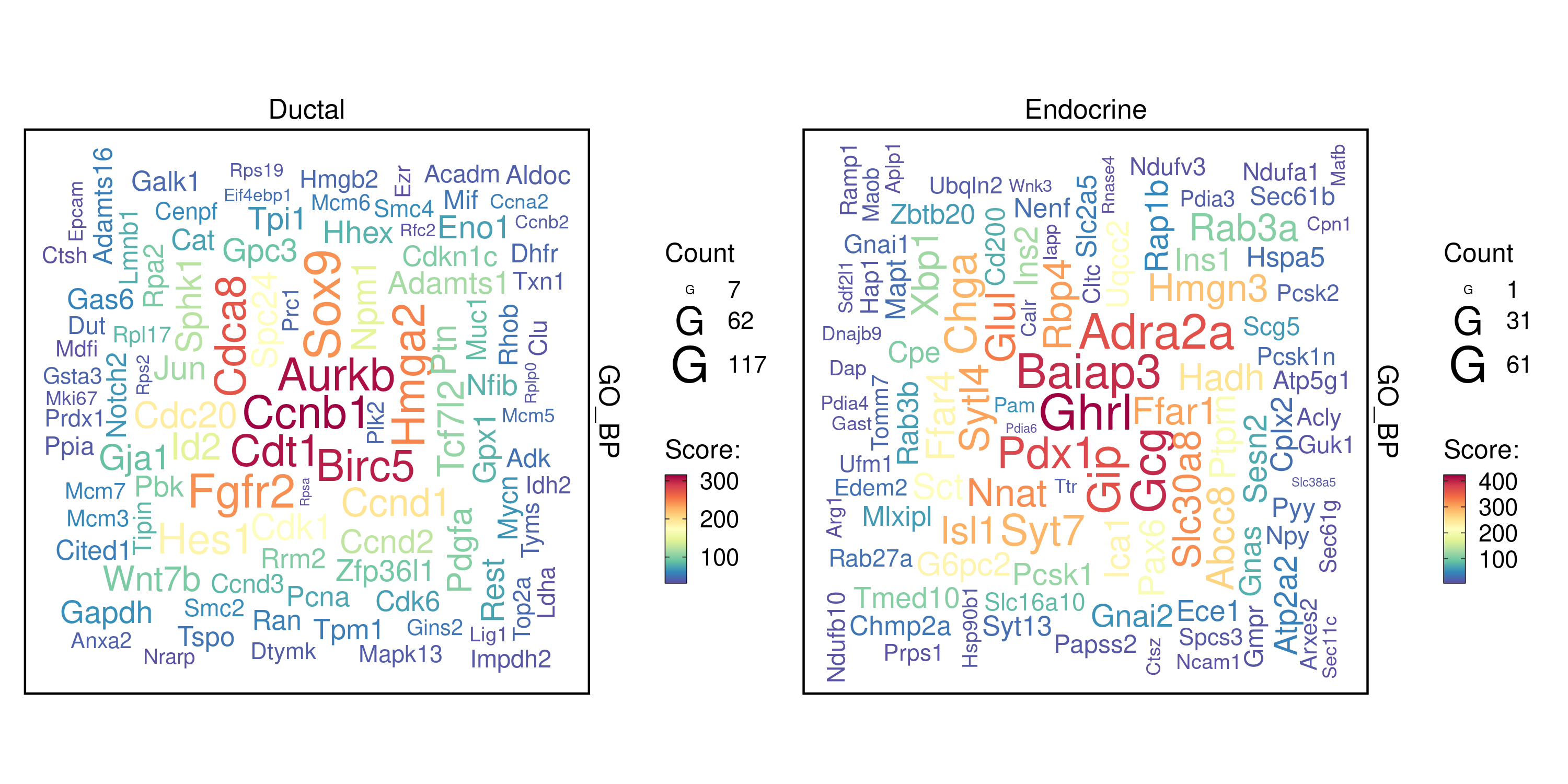
plot_type = "wordcloud",
word_type = "feature"
)
EnrichmentPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType",
group_use = "Ductal",
plot_type = "network"
)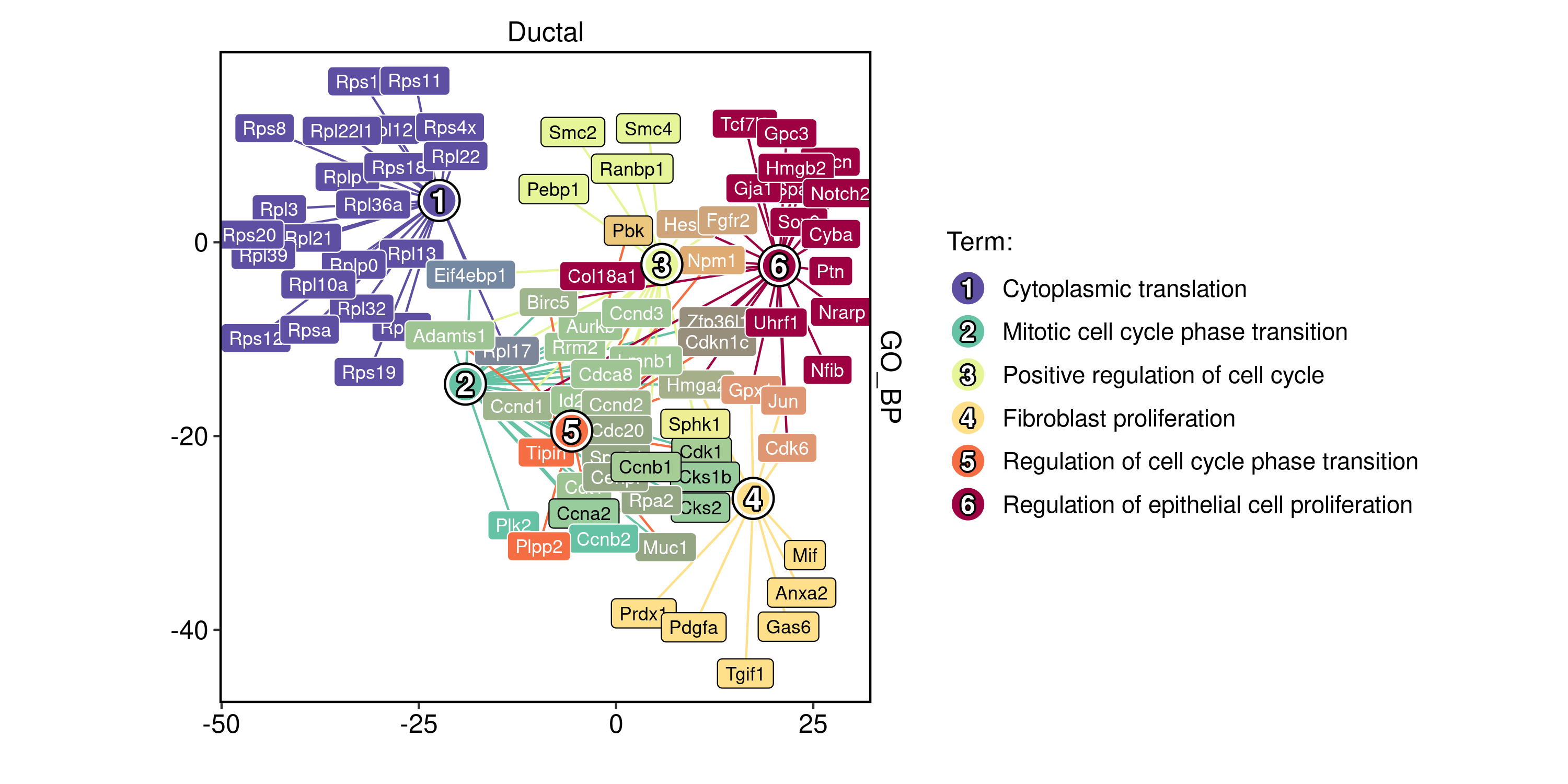
To ensure that labels are visible, you can adjust the size of the viewer panel on Rstudio IDE.
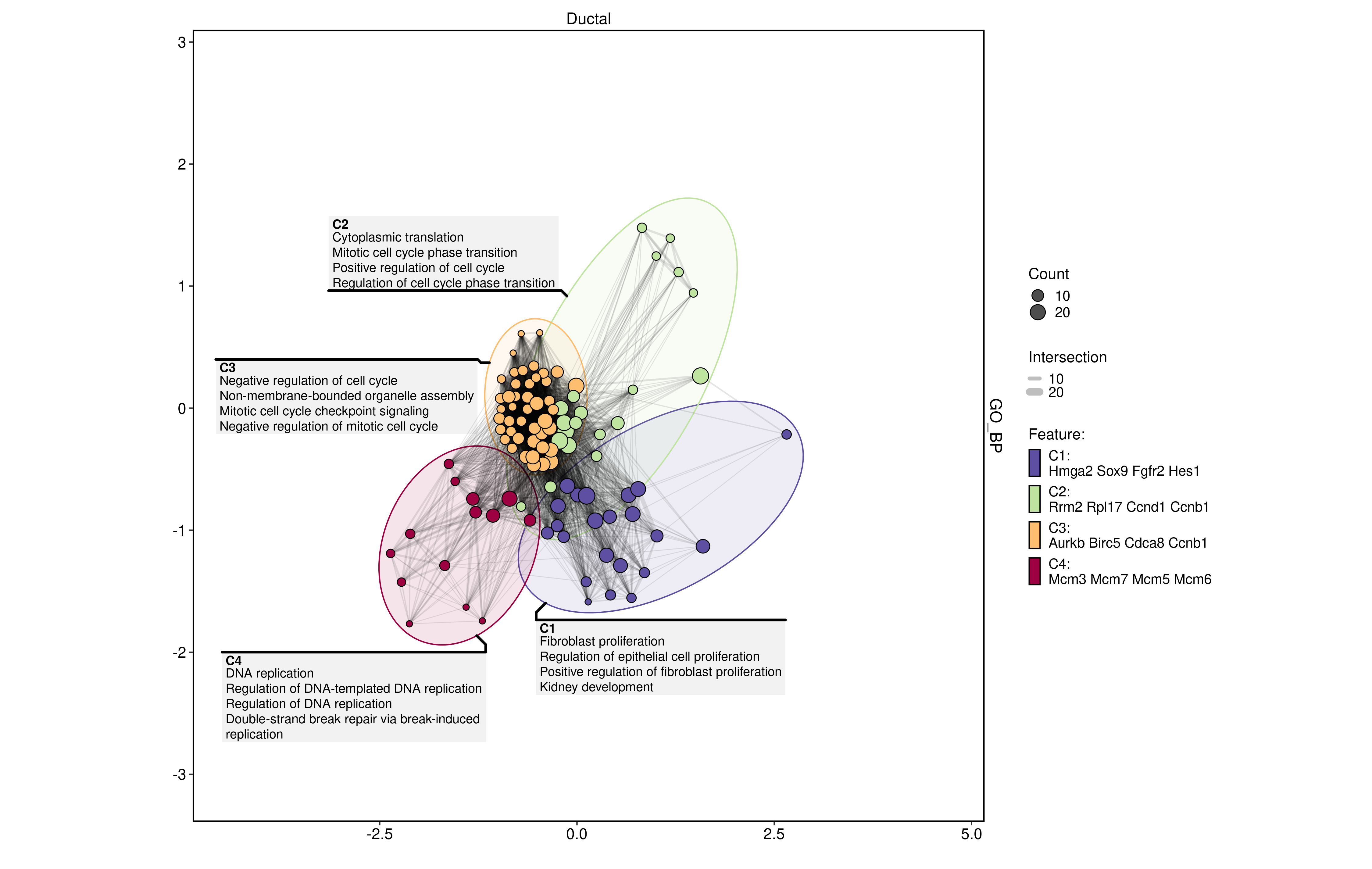
EnrichmentPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType",
group_use = "Ductal",
plot_type = "enrichmap"
)
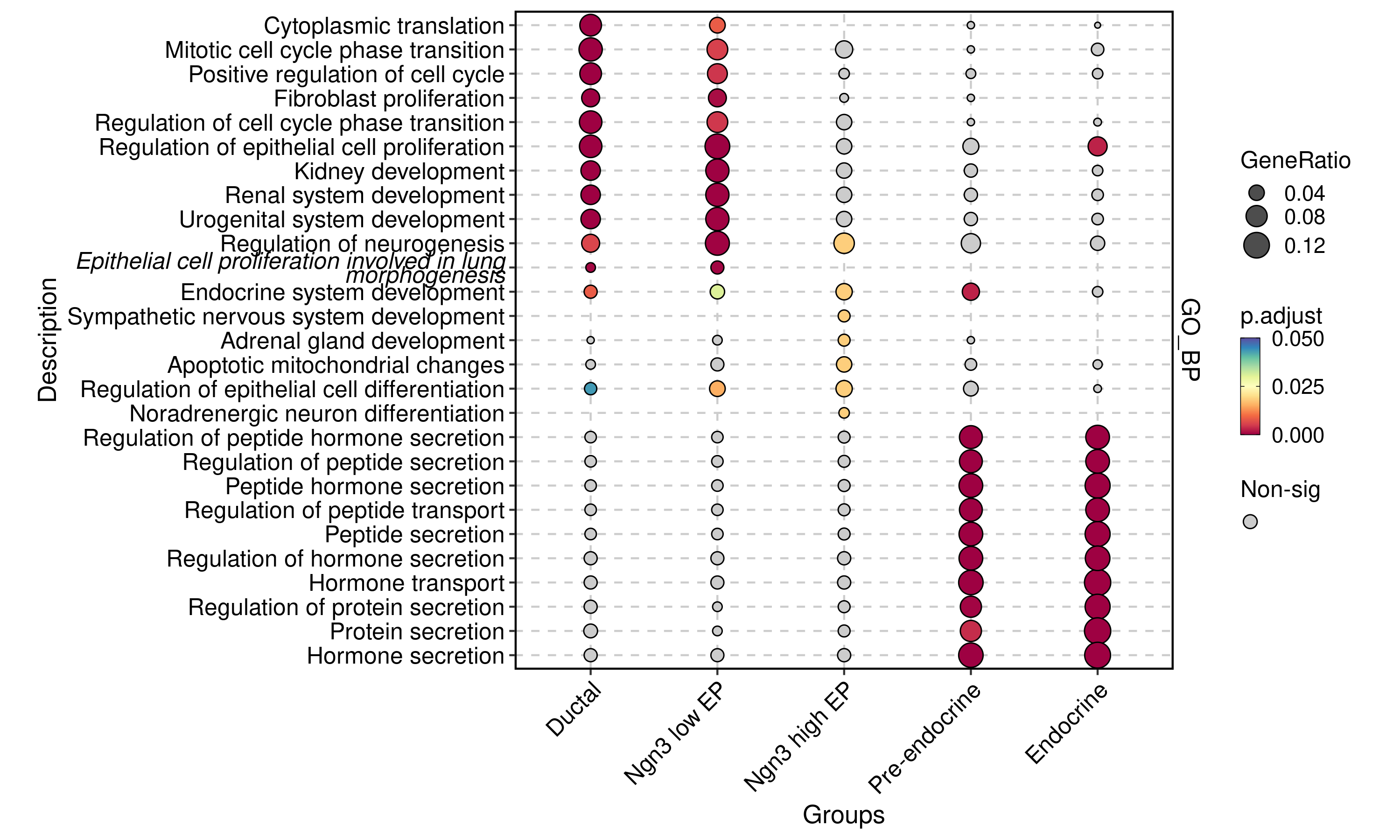
EnrichmentPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType",
plot_type = "comparison"
)
Enrichment analysis(GSEA)
pancreas_sub <- RunGSEA(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType",
db = "GO_BP",
species = "Mus_musculus",
DE_threshold = "p_val_adj < 0.05"
)
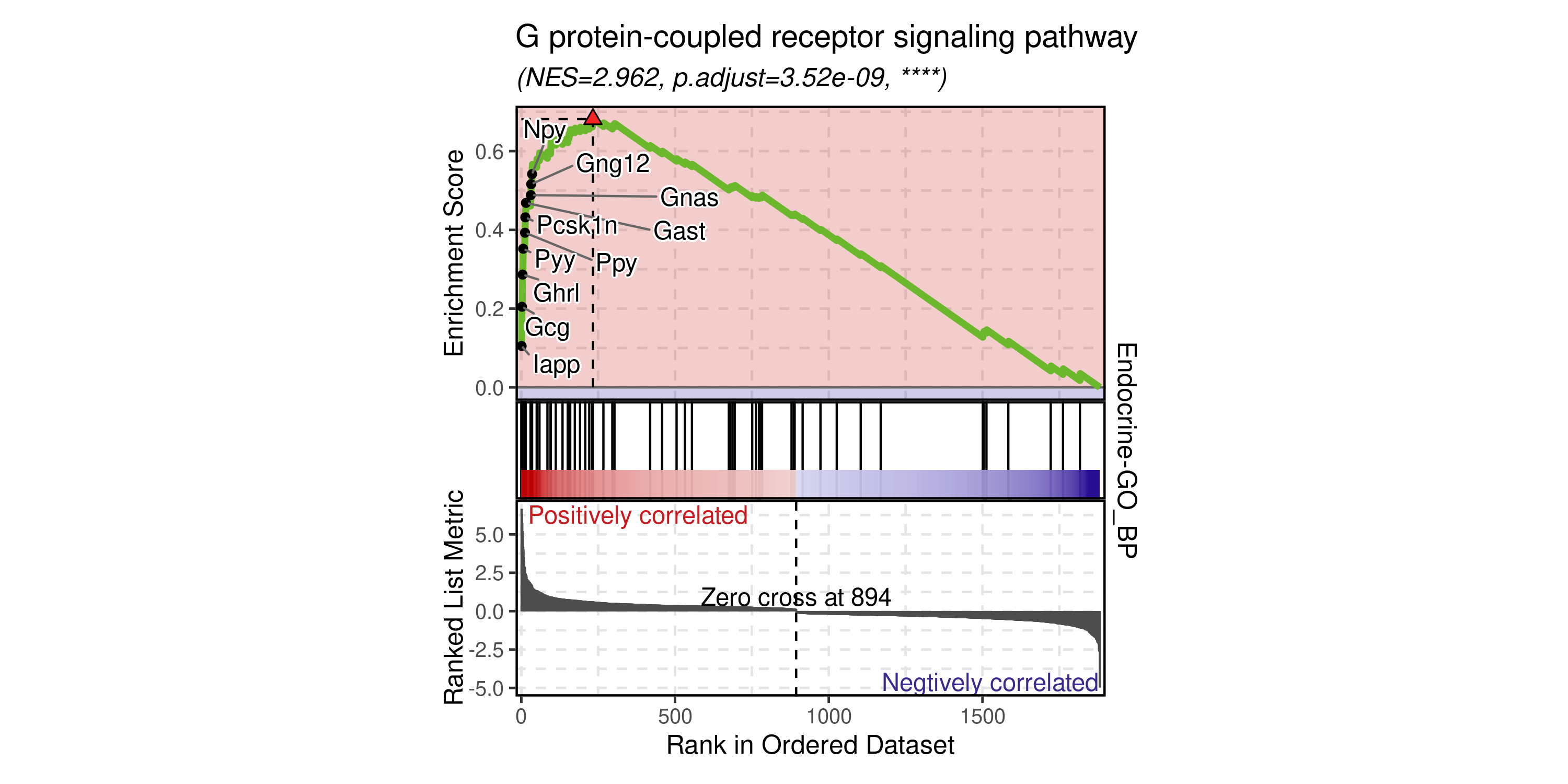
GSEAPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType",
group_use = "Endocrine",
id_use = "GO:0007186"
)
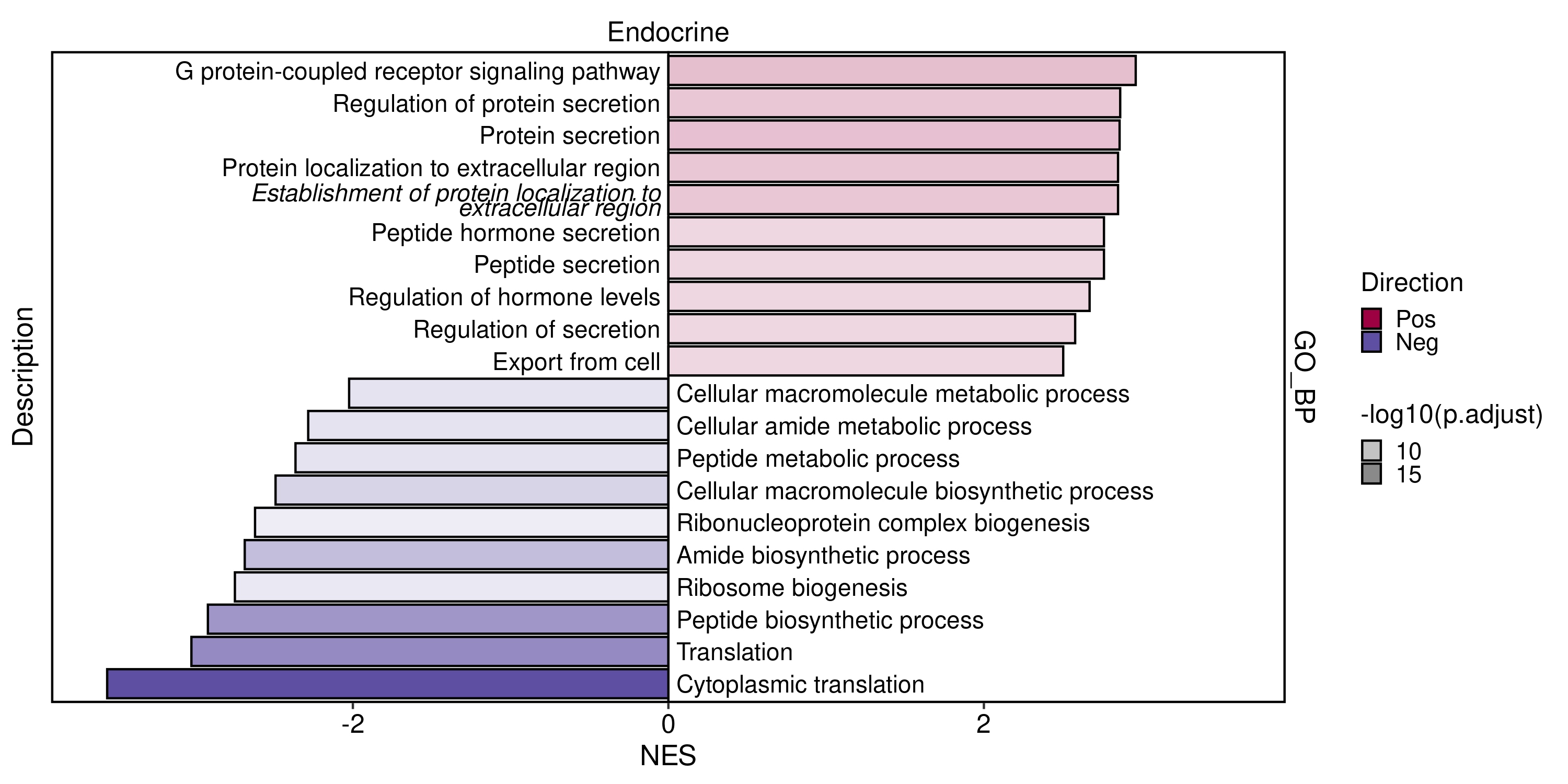
GSEAPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group_by = "CellType",
group_use = "Endocrine",
plot_type = "bar",
direction = "both",
topTerm = 20
)
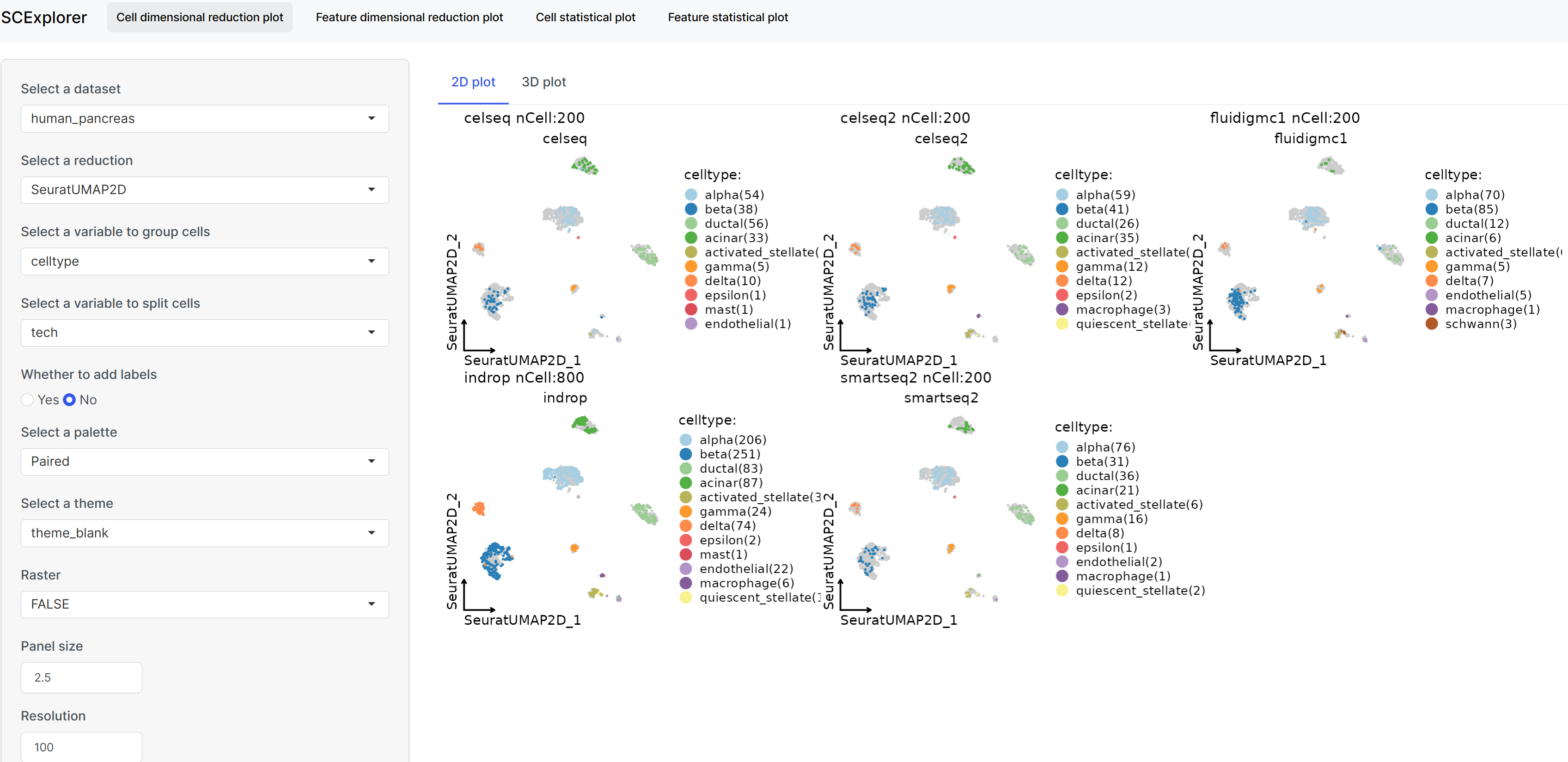
Interactive data visualization with SCExplorer
PrepareSCExplorer(
list(
mouse_pancreas = pancreas_sub,
human_pancreas = panc8_sub
),
base_dir = "./SCExplorer"
)
app <- RunSCExplorer(base_dir = "./SCExplorer")
list.files("./SCExplorer") # This directory can be used as site directory for Shiny Server.
if (interactive()) {
shiny::runApp(app)
}
Other visualization examples
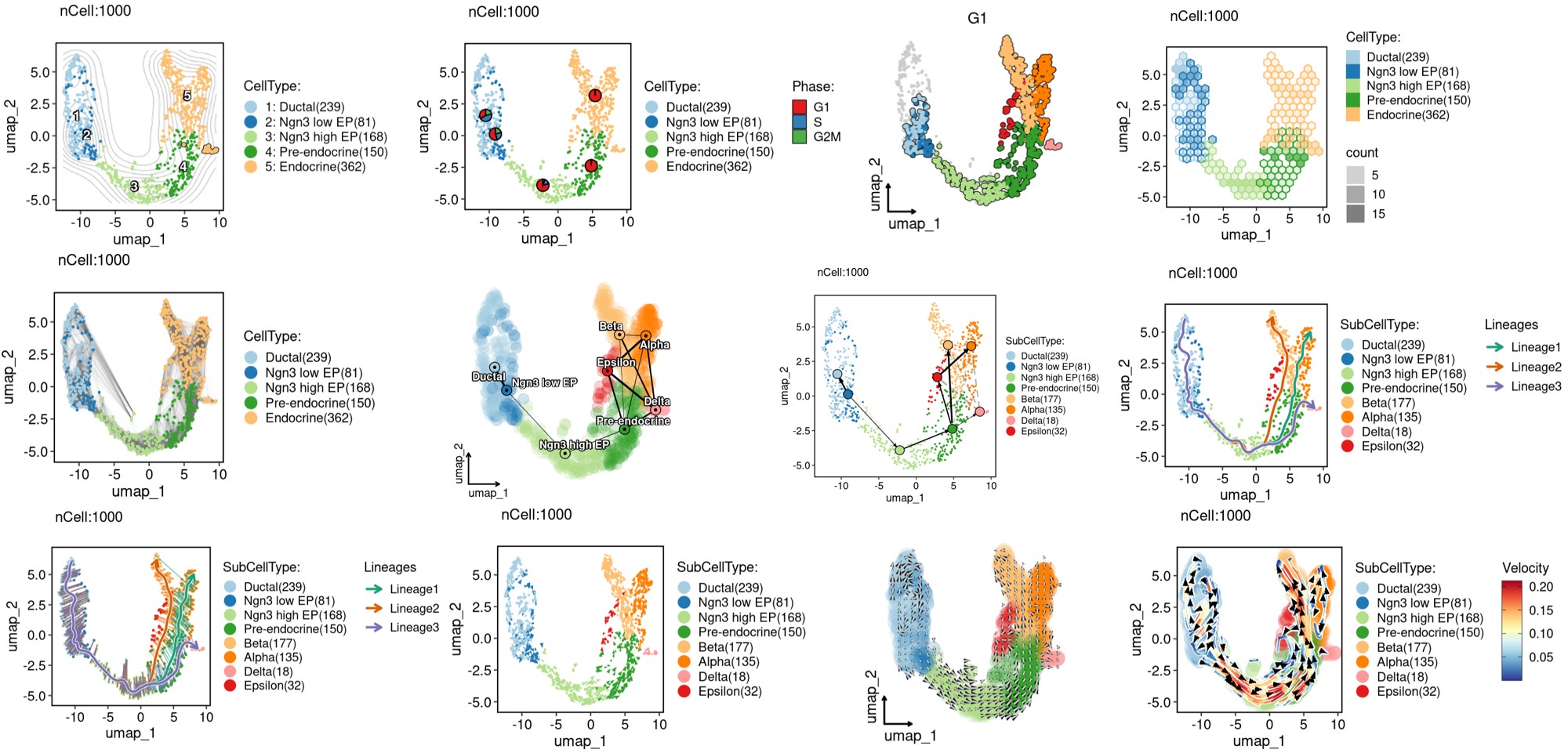 CellStatPlot
CellStatPlot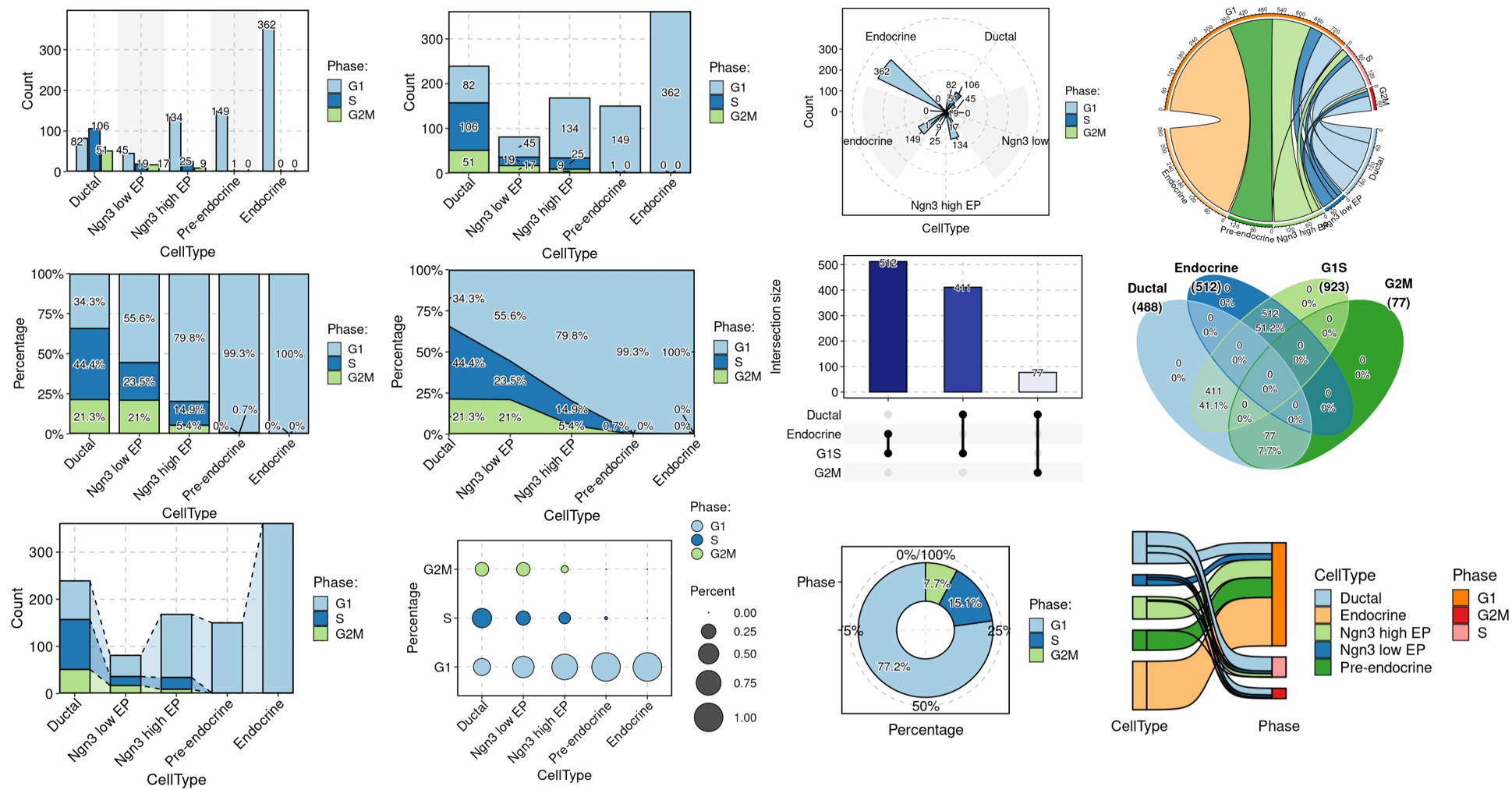 FeatureStatPlot
FeatureStatPlot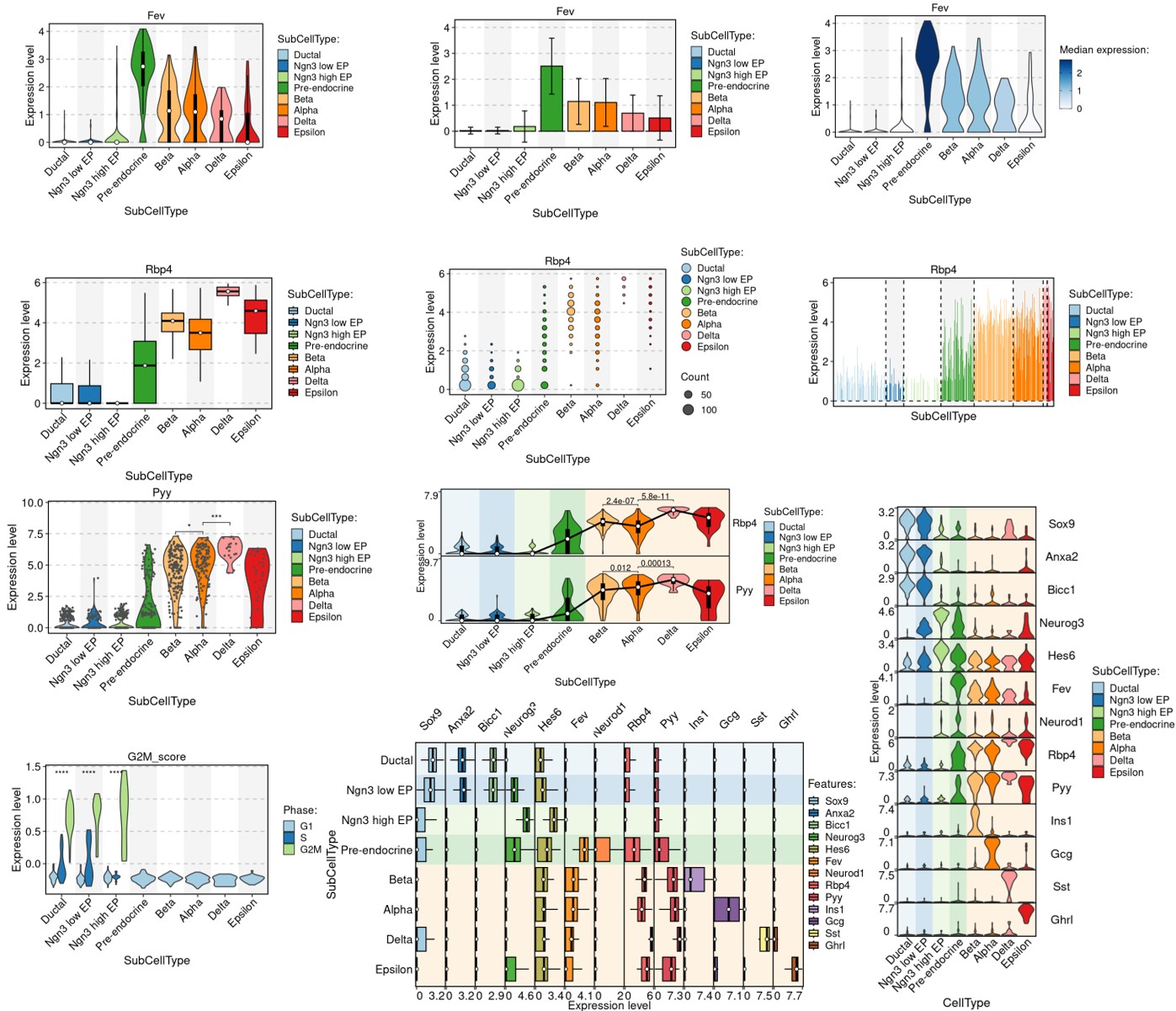 GroupHeatmap
GroupHeatmap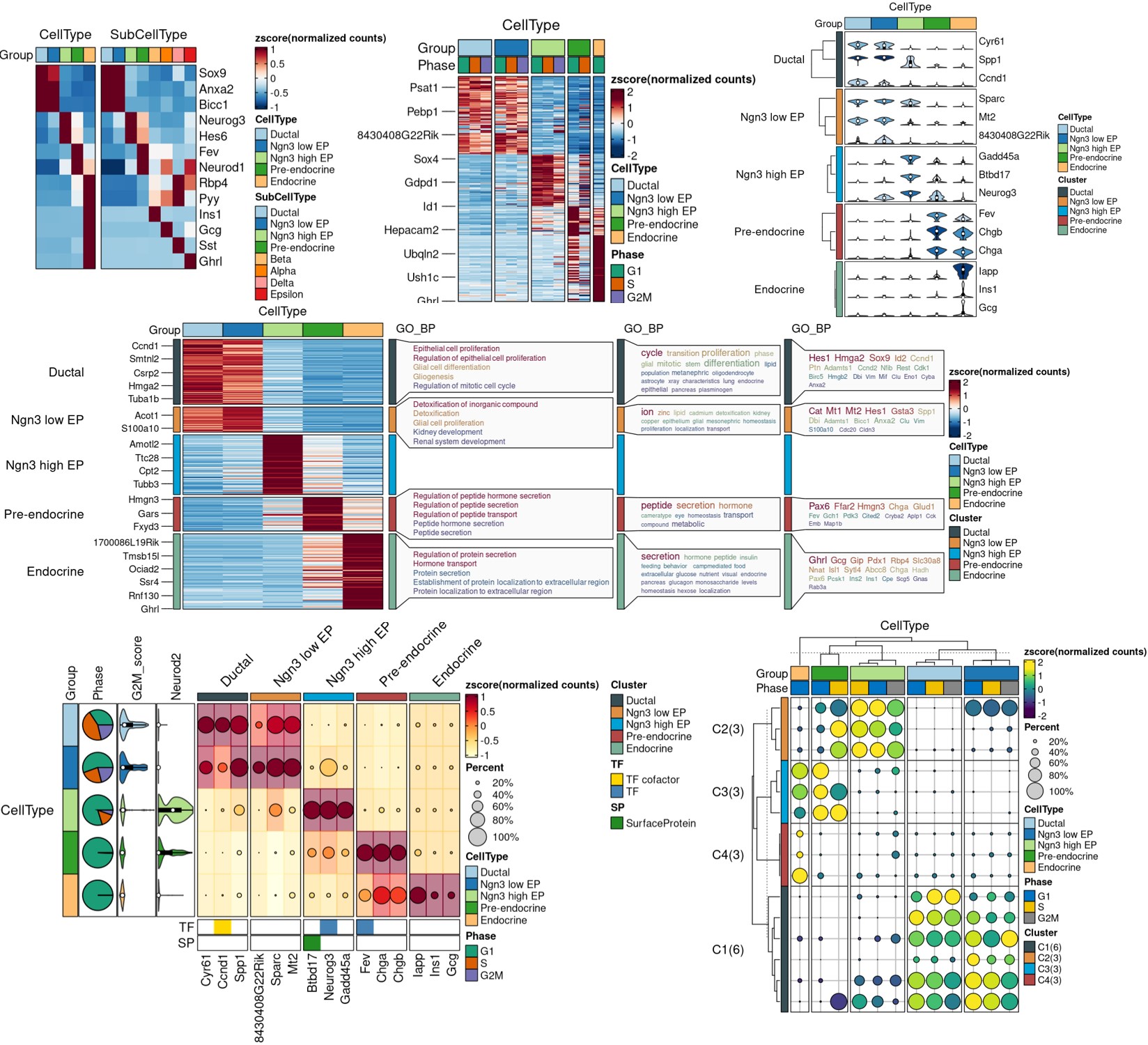
You can also find more examples in the documentation of the function: integration_scop, RunKNNMap, RunPalantir, etc.