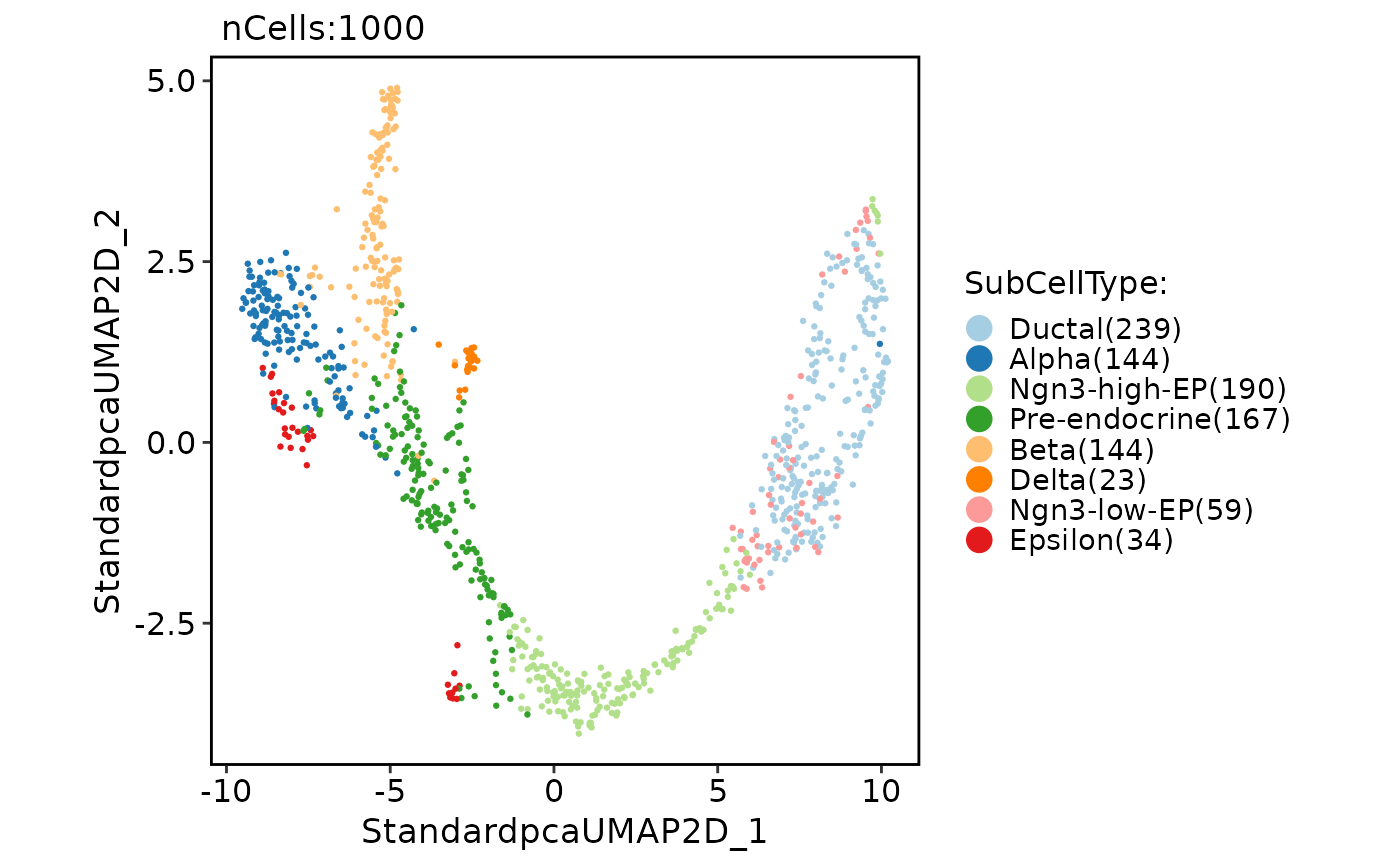
This function performs a standard single-cell analysis workflow.
Usage
standard_scop(
srt,
prefix = "Standard",
assay = NULL,
do_normalization = NULL,
normalization_method = "LogNormalize",
do_HVF_finding = TRUE,
HVF_method = "vst",
nHVF = 2000,
HVF = NULL,
do_scaling = TRUE,
vars_to_regress = NULL,
regression_model = "linear",
linear_reduction = "pca",
linear_reduction_dims = 50,
linear_reduction_dims_use = NULL,
linear_reduction_params = list(),
force_linear_reduction = FALSE,
nonlinear_reduction = "umap",
nonlinear_reduction_dims = c(2, 3),
nonlinear_reduction_params = list(),
force_nonlinear_reduction = TRUE,
neighbor_metric = "euclidean",
neighbor_k = 20L,
cluster_algorithm = "louvain",
cluster_resolution = 0.6,
verbose = TRUE,
seed = 11
)Arguments
- srt
A Seurat object.
- prefix
A prefix to add to the names of intermediate objects created by the function. Default is
"Standard".- assay
Which assay to use. If
NULL, the default assay of the Seurat object will be used.- do_normalization
Whether to perform normalization. If
NULL, normalization will be performed if the specified assay does not have scaled data.- normalization_method
The method to use for normalization. Options are
"LogNormalize","SCT", or"TFIDF". Default is"LogNormalize".- do_HVF_finding
Whether to perform high variable feature finding. If
TRUE, the function will force to find the highly variable features (HVF) using the specified HVF method.- HVF_method
The method to use for finding highly variable features. Options are
"vst","mvp", or"disp". Default is"vst".- nHVF
The number of highly variable features to select. If NULL, all highly variable features will be used. Default is
2000.- HVF
A vector of feature names to use as highly variable features. If NULL, the function will use the highly variable features identified by the HVF method.
- do_scaling
Whether to perform scaling. If
TRUE, the function will force to scale the data using the Seurat::ScaleData function.- vars_to_regress
A vector of feature names to use as regressors in the scaling step. If NULL, no regressors will be used.
- regression_model
The regression model to use for scaling. Options are
"linear","poisson", or"negativebinomial". Default is"linear".- linear_reduction
The linear dimensionality reduction method to use. Options are
"pca","svd","ica","nmf","mds", or"glmpca". Default is"pca".- linear_reduction_dims
The number of dimensions to keep after linear dimensionality reduction. Default is
50.- linear_reduction_dims_use
The dimensions to use for downstream analysis. If
NULL, all dimensions will be used.- linear_reduction_params
A list of parameters to pass to the linear dimensionality reduction method.
- force_linear_reduction
Whether to force linear dimensionality reduction even if the specified reduction is already present in the Seurat object.
- nonlinear_reduction
The nonlinear dimensionality reduction method to use. Options are
"umap","umap-naive","tsne","dm","phate","pacmap","trimap","largevis", or"fr". Default is"umap".- nonlinear_reduction_dims
The number of dimensions to keep after nonlinear dimensionality reduction. If a vector is provided, different numbers of dimensions can be specified for each method. Default is
c(2, 3).- nonlinear_reduction_params
A list of parameters to pass to the nonlinear dimensionality reduction method.
- force_nonlinear_reduction
Whether to force nonlinear dimensionality reduction even if the specified reduction is already present in the Seurat object. Default is
TRUE.- neighbor_metric
The distance metric to use for finding neighbors. Options are
"euclidean","cosine","manhattan", or"hamming". Default is"euclidean".- neighbor_k
The number of nearest neighbors to use for finding neighbors. Default is
20.- cluster_algorithm
The clustering algorithm to use. Options are
"louvain","slm", or"leiden". Default is"louvain".- cluster_resolution
The resolution parameter to use for clustering. Larger values result in fewer clusters. Default is
0.6.- verbose
Whether to print the message. Default is
TRUE.- seed
Random seed for reproducibility. Default is
11.
Examples
library(Matrix)
data(pancreas_sub)
pancreas_sub <- standard_scop(pancreas_sub)
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:45] Start standard scop workflow...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:46] Checking a list of <Seurat>...
#> ! [2026-02-11 04:23:46] Data 1/1 of the `srt_list` is "unknown"
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:46] Perform `NormalizeData()` with `normalization.method = 'LogNormalize'` on the data 1/1 of the `srt_list`...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:48] Perform `Seurat::FindVariableFeatures()` on the data 1/1 of the `srt_list`...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:48] Use the separate HVF from srt_list
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:49] Number of available HVF: 2000
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:49] Finished check
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:49] Perform `Seurat::ScaleData()`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:49] Perform pca linear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:50] Perform `Seurat::FindClusters()` with `cluster_algorithm = 'louvain'` and `cluster_resolution = 0.6`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:50] Reorder clusters...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:50] Perform umap nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:50] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:23:55] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ✔ [2026-02-11 04:24:00] Run scop standard workflow completed
CellDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "SubCellType"
)
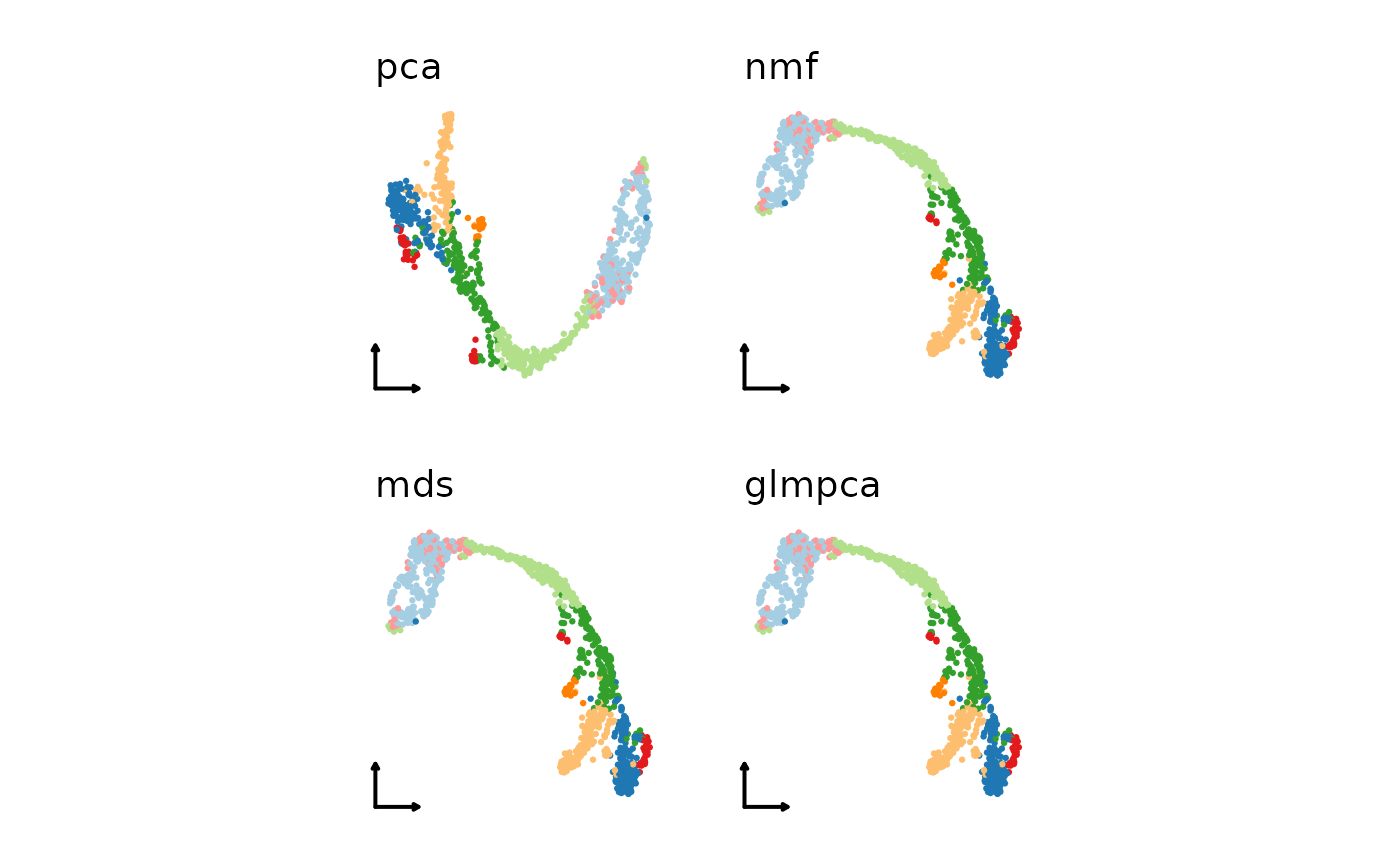
 # Use a combination of different linear
# or non-linear dimension reduction methods
linear_reductions <- c(
"pca", "nmf", "mds"
)
pancreas_sub <- standard_scop(
pancreas_sub,
linear_reduction = linear_reductions,
nonlinear_reduction = "umap"
)
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:00] Start standard scop workflow...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:00] Checking a list of <Seurat>...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:00] Data 1/1 of the `srt_list` has been log-normalized
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:00] Perform `Seurat::FindVariableFeatures()` on the data 1/1 of the `srt_list`...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:01] Use the separate HVF from srt_list
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:01] Number of available HVF: 2000
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:01] Finished check
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:01] Perform `Seurat::ScaleData()`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:01] Perform pca linear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:02] Perform `Seurat::FindClusters()` with `cluster_algorithm = 'louvain'` and `cluster_resolution = 0.6`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:02] Reorder clusters...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:03] Perform umap nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:03] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:07] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:12] Perform nmf linear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:12] Running NMF...
#> ℹ StandardBE_ 1
#> ℹ Positive: Ccnd1, Spp1, Mdk, Rps2, Ldha, Pebp1, Cd24a, Dlk1, Krt8, Mgst1
#> ℹ Clu, Gapdh, Eno1, Prdx1, Cldn10, Mif, Cldn7, Npm1, Dbi, Vim
#> ℹ Sox9, Rpl12, Aldh1b1, Rplp1, Wfdc2, Krt18, Tkt, Aldoa, Hspe1, Ptma
#> ℹ Negative: Tmem108, Poc1a, Epn3, Wipi1, Tmcc3, Nhsl1, Fgf12, Plekho1, Tecpr2, Zbtb4
#> ℹ Gm10941, Trf, Man1c1, Hmgcs1, Nipal1, Jam3, Pgap1, Alpl, Kcnip3, Tnr
#> ℹ Gm15915, Rbp2, Cbfa2t2, Sh2d4a, Bbc3, Megf6, Naaladl2, Fam46d, Hist2h2ac, Tox2
#> ℹ StandardBE_ 2
#> ℹ Positive: Spp1, Gsta3, Sparc, Vim, Atp1b1, Mt1, Dbi, Anxa2, Rps2, Id2
#> ℹ Rpl22l1, Rplp1, Mgst1, Clu, Sox9, Cldn6, Mdk, Pdzk1ip1, Bicc1, 1700011H14Rik
#> ℹ Rps12, S100a10, Cldn3, Rpl36a, Ppp1r1b, Adamts1, Serpinh1, Mt2, Ifitm2, Rpl39
#> ℹ Negative: Rpa3, Aacs, Tmem108, Poc1a, Epn3, Wipi1, B830012L14Rik, Tmcc3, Wsb1, Plekho1
#> ℹ Ppp2r2b, Tecpr2, Zbtb4, Haus8, Trf, Gm5420, Man1c1, Hmgcs1, Nipal1, Jam3
#> ℹ Tcerg1, Pgap1, Snrpa1, Alpl, Larp1b, Kcnip3, Tnr, Lsm12, Ptbp3, Gm15915
#> ℹ StandardBE_ 3
#> ℹ Positive: Cck, Mdk, Gadd45a, Neurog3, Selm, Sox4, Btbd17, Tmsb4x, Btg2, Cldn6
#> ℹ Cotl1, Ptma, Jun, Ppp1r14a, Rps2, Ifitm2, Neurod2, Igfbpl1, Gnas, Krt7
#> ℹ Nkx6-1, Aplp1, Ppp3ca, Lrpap1, Rplp1, Hn1, Rps12, Mfng, BC023829, Smarcd2
#> ℹ Negative: Elovl6, Tmem108, Poc1a, Epn3, Nop56, Wipi1, B830012L14Rik, Rrp15, Rfc1, Fgf12
#> ℹ Slc20a1, Ppp2r2b, Lama1, Tecpr2, Zbtb4, Eif1ax, Fam162a, P4ha3, Gm10941, Tenm4
#> ℹ Pde4b, Gm5420, Man1c1, Hmgcs1, Pgap1, Mgst2, Larp1b, Kcnip3, Tnr, Lsm12
#> ℹ StandardBE_ 4
#> ℹ Positive: Spp1, Cyr61, Krt18, Tpm1, Krt8, Myl12a, Vim, Jun, Anxa5, Tnfrsf12a
#> ℹ Csrp1, Sparc, Cldn7, Nudt19, Anxa2, Clu, Myl9, Atp1b1, Cldn3, Tagln2
#> ℹ S100a10, 1700011H14Rik, Cd24a, Rps2, Dbi, Id2, Lurap1l, Rplp1, Myl12b, Klf6
#> ℹ Negative: Rpa3, Elovl6, Aacs, Tmem108, Poc1a, Tmcc3, Rfc1, Plekho1, Slc20a1, Ppp2r2b
#> ℹ Lama1, Tecpr2, Gm10941, Tenm4, Pde4b, Man1c1, Nipal1, Jam3, Pgap1, Alpl
#> ℹ Mgst2, Kcnip3, Tnr, Ptbp3, Gm15915, Cntln, Ocln, Fras1, Rbp2, Cbfa2t2
#> ℹ StandardBE_ 5
#> ℹ Positive: 2810417H13Rik, Rrm2, Hmgb2, Dut, Pcna, Lig1, H2afz, Tipin, Tuba1b, Tk1
#> ℹ Mcm5, Dek, Tyms, Gmnn, Ran, Tubb5, Rfc2, Srsf2, Ranbp1, Orc6
#> ℹ Mcm3, Uhrf1, Gins2, Dnajc9, Mcm6, Siva1, Rfc3, Mcm7, Rpa2, Ptma
#> ℹ Negative: 1110002L01Rik, Aacs, Wipi1, B830012L14Rik, Tmcc3, Trib1, Fgf12, Plekho1, Ppp2r2b, Lama1
#> ℹ Tenm4, Trf, Gm5420, Man1c1, Jam3, Mgst2, Kcnip3, Tnr, Gm15915, Cbfa2t2
#> ℹ Sh2d4a, Bbc3, Fkbp9, Ano6, Prkcb, Megf6, Fam46d, Slc52a3, Ankrd2, Tox2
#> ✔ [2026-02-11 04:24:16] NMF compute completed
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:17] Perform `Seurat::FindClusters()` with `cluster_algorithm = 'louvain'` and `cluster_resolution = 0.6`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:17] Reorder clusters...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:17] Perform umap nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:17] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardnmf) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:21] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardnmf) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:26] Perform mds linear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:27] Perform `Seurat::FindClusters()` with `cluster_algorithm = 'louvain'` and `cluster_resolution = 0.6`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:27] Reorder clusters...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:27] Perform umap nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:27] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardmds) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:32] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardmds) dims (1-50) as input
#> ✔ [2026-02-11 04:24:37] Run scop standard workflow completed
plist1 <- lapply(
linear_reductions, function(lr) {
CellDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "SubCellType",
reduction = paste0(
"Standard", lr, "UMAP2D"
),
xlab = "", ylab = "", title = lr,
legend.position = "none",
theme_use = "theme_blank"
)
}
)
patchwork::wrap_plots(plist1)
# Use a combination of different linear
# or non-linear dimension reduction methods
linear_reductions <- c(
"pca", "nmf", "mds"
)
pancreas_sub <- standard_scop(
pancreas_sub,
linear_reduction = linear_reductions,
nonlinear_reduction = "umap"
)
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:00] Start standard scop workflow...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:00] Checking a list of <Seurat>...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:00] Data 1/1 of the `srt_list` has been log-normalized
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:00] Perform `Seurat::FindVariableFeatures()` on the data 1/1 of the `srt_list`...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:01] Use the separate HVF from srt_list
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:01] Number of available HVF: 2000
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:01] Finished check
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:01] Perform `Seurat::ScaleData()`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:01] Perform pca linear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:02] Perform `Seurat::FindClusters()` with `cluster_algorithm = 'louvain'` and `cluster_resolution = 0.6`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:02] Reorder clusters...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:03] Perform umap nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:03] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:07] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:12] Perform nmf linear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:12] Running NMF...
#> ℹ StandardBE_ 1
#> ℹ Positive: Ccnd1, Spp1, Mdk, Rps2, Ldha, Pebp1, Cd24a, Dlk1, Krt8, Mgst1
#> ℹ Clu, Gapdh, Eno1, Prdx1, Cldn10, Mif, Cldn7, Npm1, Dbi, Vim
#> ℹ Sox9, Rpl12, Aldh1b1, Rplp1, Wfdc2, Krt18, Tkt, Aldoa, Hspe1, Ptma
#> ℹ Negative: Tmem108, Poc1a, Epn3, Wipi1, Tmcc3, Nhsl1, Fgf12, Plekho1, Tecpr2, Zbtb4
#> ℹ Gm10941, Trf, Man1c1, Hmgcs1, Nipal1, Jam3, Pgap1, Alpl, Kcnip3, Tnr
#> ℹ Gm15915, Rbp2, Cbfa2t2, Sh2d4a, Bbc3, Megf6, Naaladl2, Fam46d, Hist2h2ac, Tox2
#> ℹ StandardBE_ 2
#> ℹ Positive: Spp1, Gsta3, Sparc, Vim, Atp1b1, Mt1, Dbi, Anxa2, Rps2, Id2
#> ℹ Rpl22l1, Rplp1, Mgst1, Clu, Sox9, Cldn6, Mdk, Pdzk1ip1, Bicc1, 1700011H14Rik
#> ℹ Rps12, S100a10, Cldn3, Rpl36a, Ppp1r1b, Adamts1, Serpinh1, Mt2, Ifitm2, Rpl39
#> ℹ Negative: Rpa3, Aacs, Tmem108, Poc1a, Epn3, Wipi1, B830012L14Rik, Tmcc3, Wsb1, Plekho1
#> ℹ Ppp2r2b, Tecpr2, Zbtb4, Haus8, Trf, Gm5420, Man1c1, Hmgcs1, Nipal1, Jam3
#> ℹ Tcerg1, Pgap1, Snrpa1, Alpl, Larp1b, Kcnip3, Tnr, Lsm12, Ptbp3, Gm15915
#> ℹ StandardBE_ 3
#> ℹ Positive: Cck, Mdk, Gadd45a, Neurog3, Selm, Sox4, Btbd17, Tmsb4x, Btg2, Cldn6
#> ℹ Cotl1, Ptma, Jun, Ppp1r14a, Rps2, Ifitm2, Neurod2, Igfbpl1, Gnas, Krt7
#> ℹ Nkx6-1, Aplp1, Ppp3ca, Lrpap1, Rplp1, Hn1, Rps12, Mfng, BC023829, Smarcd2
#> ℹ Negative: Elovl6, Tmem108, Poc1a, Epn3, Nop56, Wipi1, B830012L14Rik, Rrp15, Rfc1, Fgf12
#> ℹ Slc20a1, Ppp2r2b, Lama1, Tecpr2, Zbtb4, Eif1ax, Fam162a, P4ha3, Gm10941, Tenm4
#> ℹ Pde4b, Gm5420, Man1c1, Hmgcs1, Pgap1, Mgst2, Larp1b, Kcnip3, Tnr, Lsm12
#> ℹ StandardBE_ 4
#> ℹ Positive: Spp1, Cyr61, Krt18, Tpm1, Krt8, Myl12a, Vim, Jun, Anxa5, Tnfrsf12a
#> ℹ Csrp1, Sparc, Cldn7, Nudt19, Anxa2, Clu, Myl9, Atp1b1, Cldn3, Tagln2
#> ℹ S100a10, 1700011H14Rik, Cd24a, Rps2, Dbi, Id2, Lurap1l, Rplp1, Myl12b, Klf6
#> ℹ Negative: Rpa3, Elovl6, Aacs, Tmem108, Poc1a, Tmcc3, Rfc1, Plekho1, Slc20a1, Ppp2r2b
#> ℹ Lama1, Tecpr2, Gm10941, Tenm4, Pde4b, Man1c1, Nipal1, Jam3, Pgap1, Alpl
#> ℹ Mgst2, Kcnip3, Tnr, Ptbp3, Gm15915, Cntln, Ocln, Fras1, Rbp2, Cbfa2t2
#> ℹ StandardBE_ 5
#> ℹ Positive: 2810417H13Rik, Rrm2, Hmgb2, Dut, Pcna, Lig1, H2afz, Tipin, Tuba1b, Tk1
#> ℹ Mcm5, Dek, Tyms, Gmnn, Ran, Tubb5, Rfc2, Srsf2, Ranbp1, Orc6
#> ℹ Mcm3, Uhrf1, Gins2, Dnajc9, Mcm6, Siva1, Rfc3, Mcm7, Rpa2, Ptma
#> ℹ Negative: 1110002L01Rik, Aacs, Wipi1, B830012L14Rik, Tmcc3, Trib1, Fgf12, Plekho1, Ppp2r2b, Lama1
#> ℹ Tenm4, Trf, Gm5420, Man1c1, Jam3, Mgst2, Kcnip3, Tnr, Gm15915, Cbfa2t2
#> ℹ Sh2d4a, Bbc3, Fkbp9, Ano6, Prkcb, Megf6, Fam46d, Slc52a3, Ankrd2, Tox2
#> ✔ [2026-02-11 04:24:16] NMF compute completed
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:17] Perform `Seurat::FindClusters()` with `cluster_algorithm = 'louvain'` and `cluster_resolution = 0.6`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:17] Reorder clusters...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:17] Perform umap nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:17] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardnmf) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:21] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardnmf) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:26] Perform mds linear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:27] Perform `Seurat::FindClusters()` with `cluster_algorithm = 'louvain'` and `cluster_resolution = 0.6`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:27] Reorder clusters...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:27] Perform umap nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:27] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardmds) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:32] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardmds) dims (1-50) as input
#> ✔ [2026-02-11 04:24:37] Run scop standard workflow completed
plist1 <- lapply(
linear_reductions, function(lr) {
CellDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "SubCellType",
reduction = paste0(
"Standard", lr, "UMAP2D"
),
xlab = "", ylab = "", title = lr,
legend.position = "none",
theme_use = "theme_blank"
)
}
)
patchwork::wrap_plots(plist1)
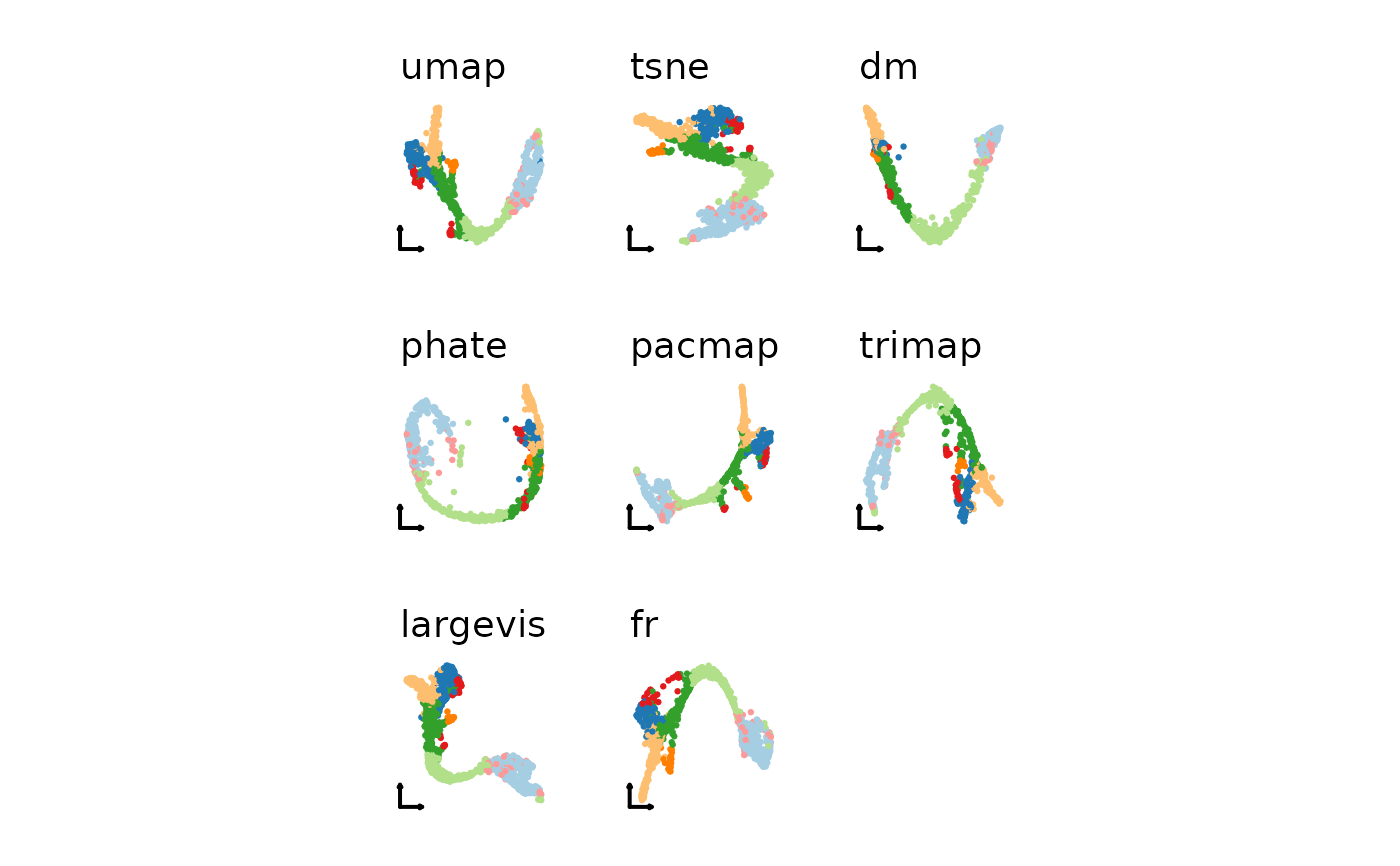
 nonlinear_reductions <- c(
"umap", "tsne", "fr"
)
pancreas_sub <- standard_scop(
pancreas_sub,
linear_reduction = "pca",
nonlinear_reduction = nonlinear_reductions
)
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:37] Start standard scop workflow...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:37] Checking a list of <Seurat>...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:38] Data 1/1 of the `srt_list` has been log-normalized
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:38] Perform `Seurat::FindVariableFeatures()` on the data 1/1 of the `srt_list`...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:38] Use the separate HVF from srt_list
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:38] Number of available HVF: 2000
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:38] Finished check
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:39] Perform `Seurat::ScaleData()`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:39] Perform pca linear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:40] Perform `Seurat::FindClusters()` with `cluster_algorithm = 'louvain'` and `cluster_resolution = 0.6`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:40] Reorder clusters...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:40] Perform umap nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:40] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:45] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:49] Perform tsne nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:49] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (tsne) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:51] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (tsne) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:55] Perform fr nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:55] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (fr) using (Standardpca_SNN) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:56] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (fr) using (Standardpca_SNN) as input
#> ✔ [2026-02-11 04:24:58] Run scop standard workflow completed
plist2 <- lapply(
nonlinear_reductions, function(nr) {
CellDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "SubCellType",
reduction = paste0(
"Standardpca", nr, "2D"
),
xlab = "", ylab = "", title = nr,
legend.position = "none",
theme_use = "theme_blank"
)
}
)
patchwork::wrap_plots(plist2)
nonlinear_reductions <- c(
"umap", "tsne", "fr"
)
pancreas_sub <- standard_scop(
pancreas_sub,
linear_reduction = "pca",
nonlinear_reduction = nonlinear_reductions
)
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:37] Start standard scop workflow...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:37] Checking a list of <Seurat>...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:38] Data 1/1 of the `srt_list` has been log-normalized
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:38] Perform `Seurat::FindVariableFeatures()` on the data 1/1 of the `srt_list`...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:38] Use the separate HVF from srt_list
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:38] Number of available HVF: 2000
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:38] Finished check
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:39] Perform `Seurat::ScaleData()`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:39] Perform pca linear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:40] Perform `Seurat::FindClusters()` with `cluster_algorithm = 'louvain'` and `cluster_resolution = 0.6`
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:40] Reorder clusters...
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:40] Perform umap nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:40] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:45] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (umap) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:49] Perform tsne nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:49] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (tsne) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:51] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (tsne) using (Standardpca) dims (1-50) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:55] Perform fr nonlinear dimension reduction
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:55] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (fr) using (Standardpca_SNN) as input
#> ℹ [2026-02-11 04:24:56] Non-linear dimensionality reduction (fr) using (Standardpca_SNN) as input
#> ✔ [2026-02-11 04:24:58] Run scop standard workflow completed
plist2 <- lapply(
nonlinear_reductions, function(nr) {
CellDimPlot(
pancreas_sub,
group.by = "SubCellType",
reduction = paste0(
"Standardpca", nr, "2D"
),
xlab = "", ylab = "", title = nr,
legend.position = "none",
theme_use = "theme_blank"
)
}
)
patchwork::wrap_plots(plist2)